VERSION HISTORY
LIRA-FEM
BIM Technology
Components of BIM technology
- New input tables have been added for setting/correcting data: dissipation coefficients, Rayleigh coefficients, an enhancing coefficient Fvk, and custom mosaic data.
- The creation of a single block of axes at the project level—with alignment to selected building floors—has been added, replacing the axes block on every floor as in previous program versions.
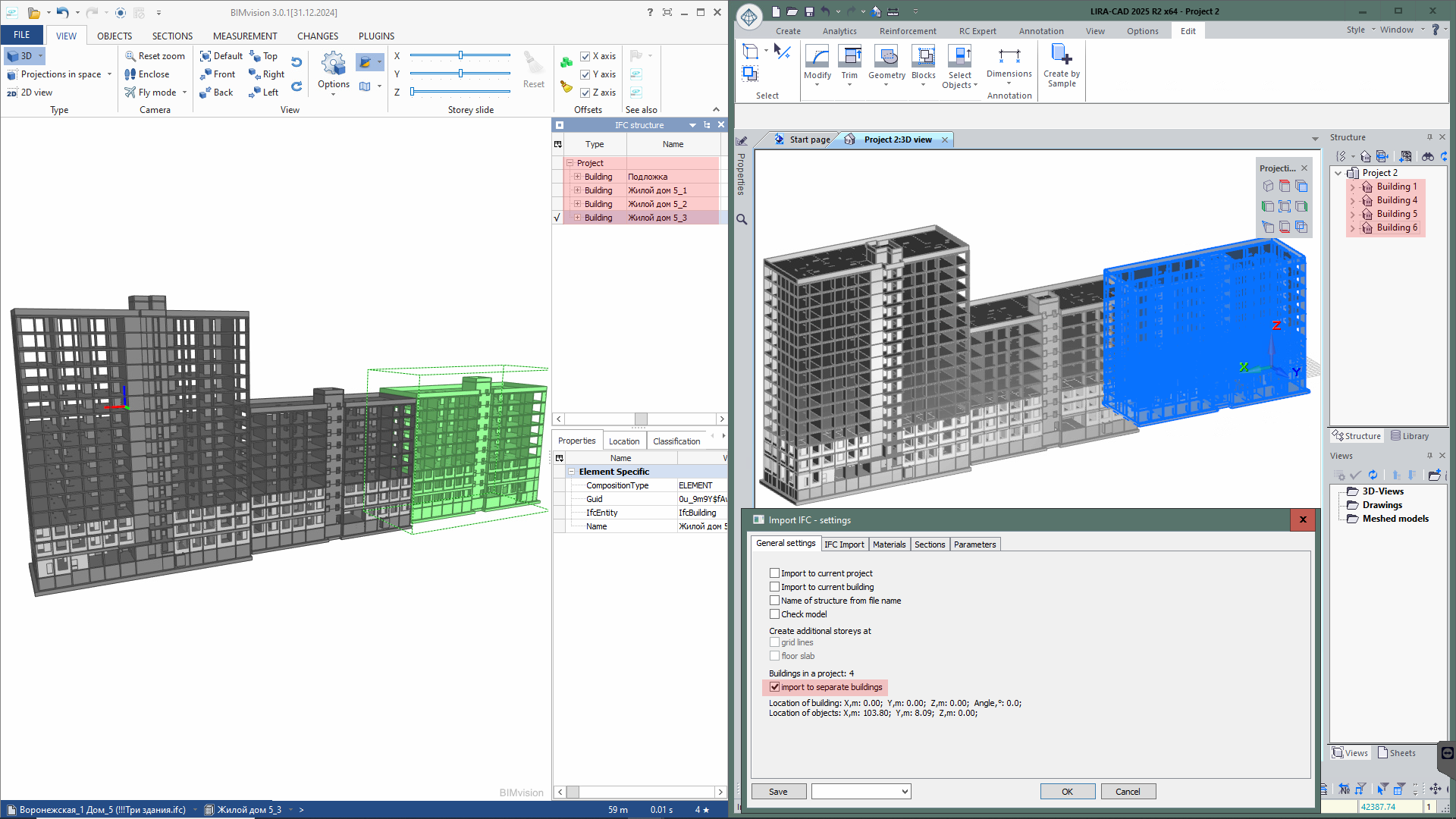
- Import of the IFC model into the configured project template has been implemented.
- When importing multiple buildings from IFC, the option to import them into separate buildings in LIRA-CAD has been added.
- The ability to import DWG floor plans into the current or a new project has been added.
- Automatic creation of openings along curved walls based on the DXF/DWG base for floor plans has been added.
- Display of the selected layer (instead of the List input name) in the “Layer Filter” node has been added.
- Improved recognition of the thickness of curved walls when constructing walls along the contour from the DXF/DWG base.
- Creation of openings along curved walls using the “Create windows at the intersection of walls and lines” node with the DXF/DWG base has been added.
- For the node “Advanced floor creation based on specified levels,” an option has been added to enable floor creation as in previous program versions (option “Upper floor levels – Yes”).
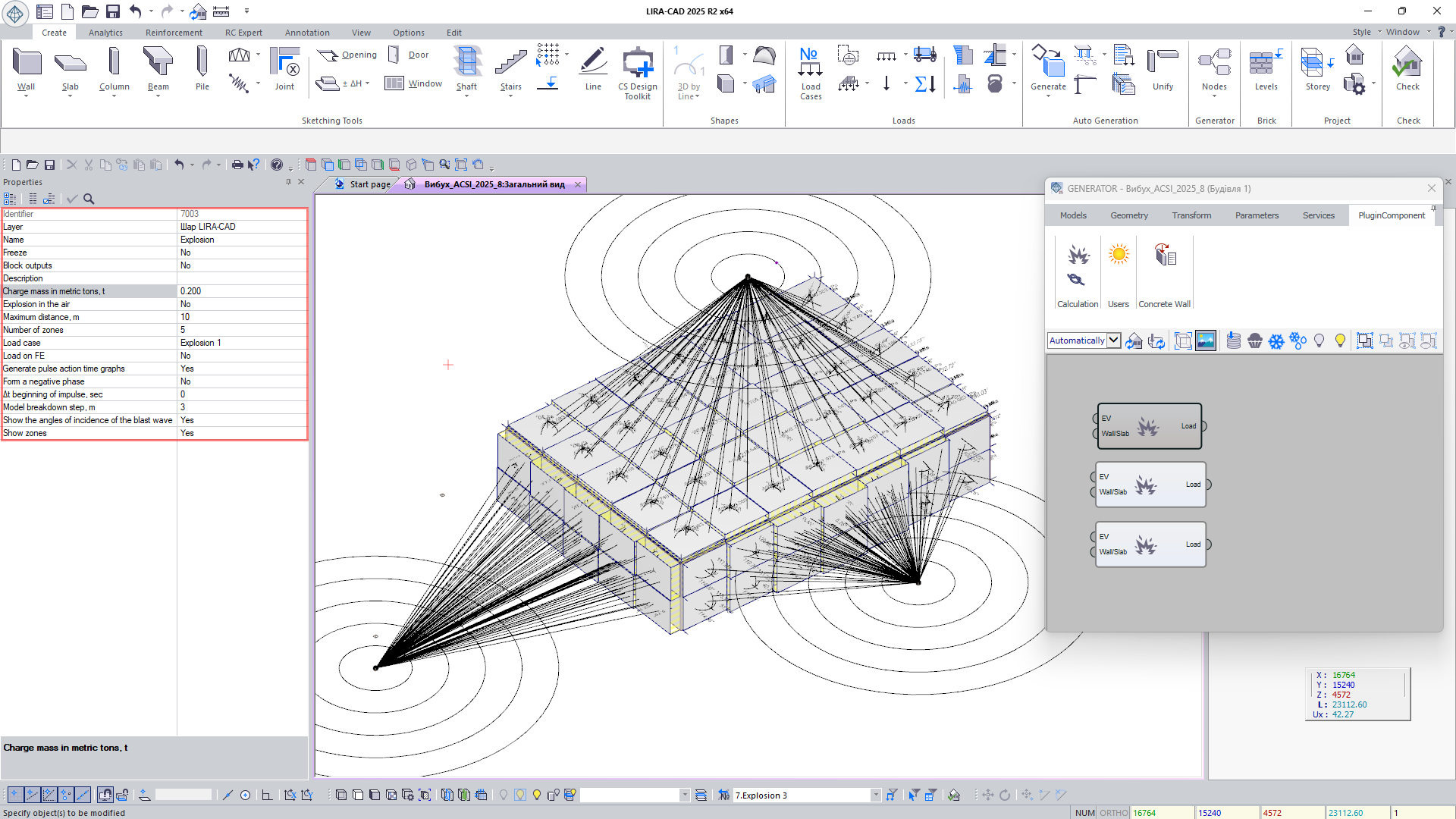
- Expanded functionality of the Blast node: an option has been added to account for or exclude the formation of a negative blast phase when constructing the graph of the explosive wave impulse’s effect (see blast analysis); for rear walls (those positioned at angles greater than 160° relative to the explosion epicenter), the gradual pressure increase caused by the shock wave’s flow along their back surface is taken into account.
Rhino (Grasshopper) Plug-in improvements
Adaptation of plug-in for integration of LIRA-CAD 2025 and Rhino 8 (Grasshopper)
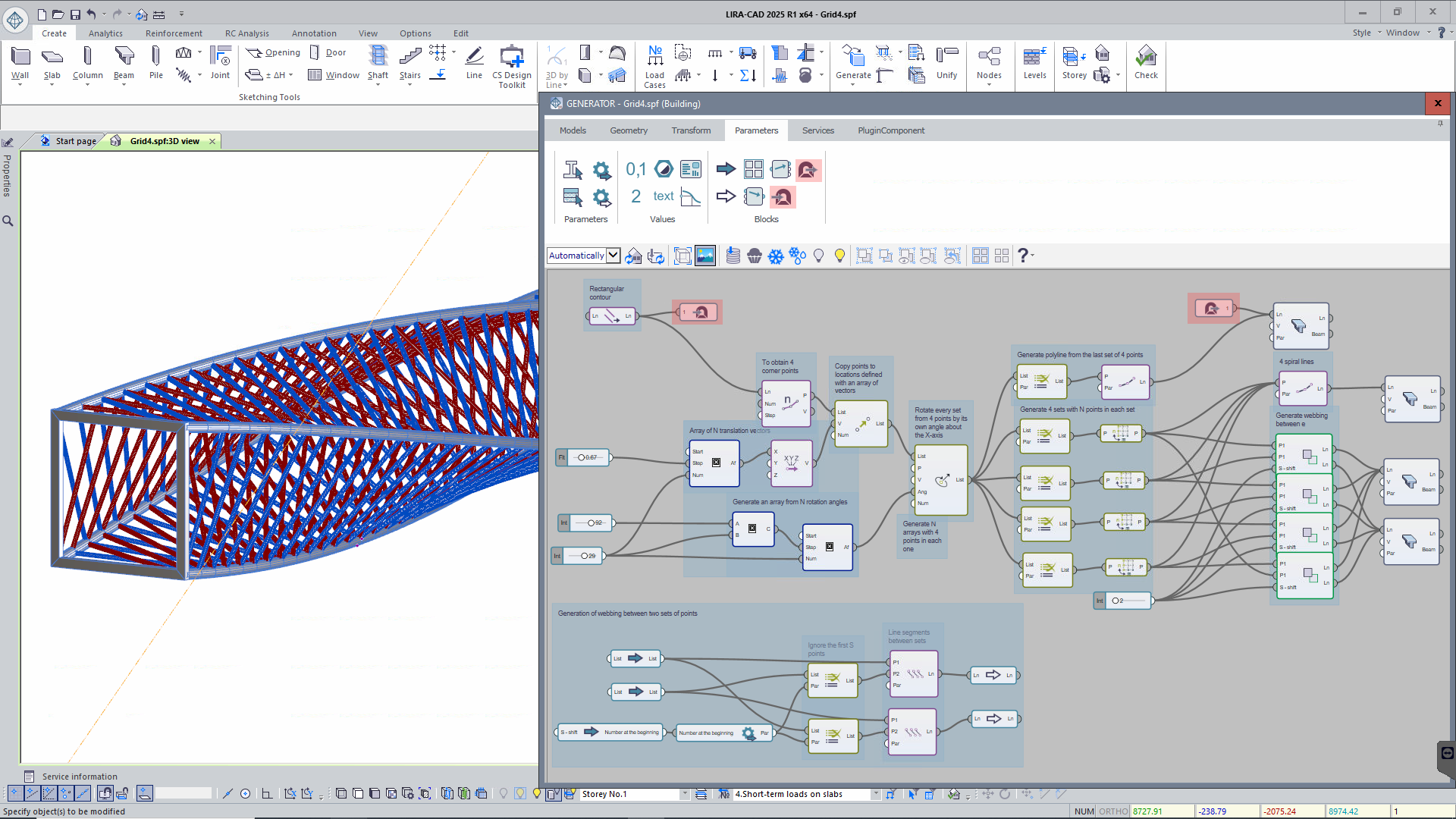
Adapted plug-in for two-way integration between LIRA-CAD 2025 and Rhino 8 (Grasshopper). This technology allows not only importing complex geometrical shapes from Grasshopper and converting them into LIRA-CAD structural objects, but also performing reverse data transfer. LIRA-CAD structural objects can serve as a basis for creating geometry in Grasshopper; it allows the user to take into account the real location of structural elements and use their geometry for accurate modelling of additional parts of the building in Grasshopper.
Interaction between LIRA-CAD module, Rhino, Revit and Archicad
Interaction between Rhino 8 (Grasshopper), Revit (Rhino.Inside.Revit), Archicad (Archicad Live Connection) and LIRA-CAD (Generator) is supported. It allows you to work with a single model and ensure data consistency at all stages of design.
New plugin features:
-
SapfirUpdate
With this node, you can only update the model in LIRA-CAD when requested, which is useful for large projects where frequent updates can hinder efficiency.
-
LoadPnt2
This node generates concentrated loads with a specified direction and intensity determined by the mutual location of two points. The load is generated between the appropriate input points, and the load value and direction depend on the distance between them.
-
LoadArea
Node for creating a non-uniformly distributed load with the option to define an arbitrary contour and taking into account the openings in the load zone.
-
LoadLine
The load allows you to define linear loads with controlled vector direction. The load can be non-uniform and the angle of application is controlled by the direction vector. You could define the objects that the load will be applied to.
-
LoadPnt
Node for specifying point loads, where the user defines the coordinates of the point at which the load is applied to, the direction of the load vector and the load value.
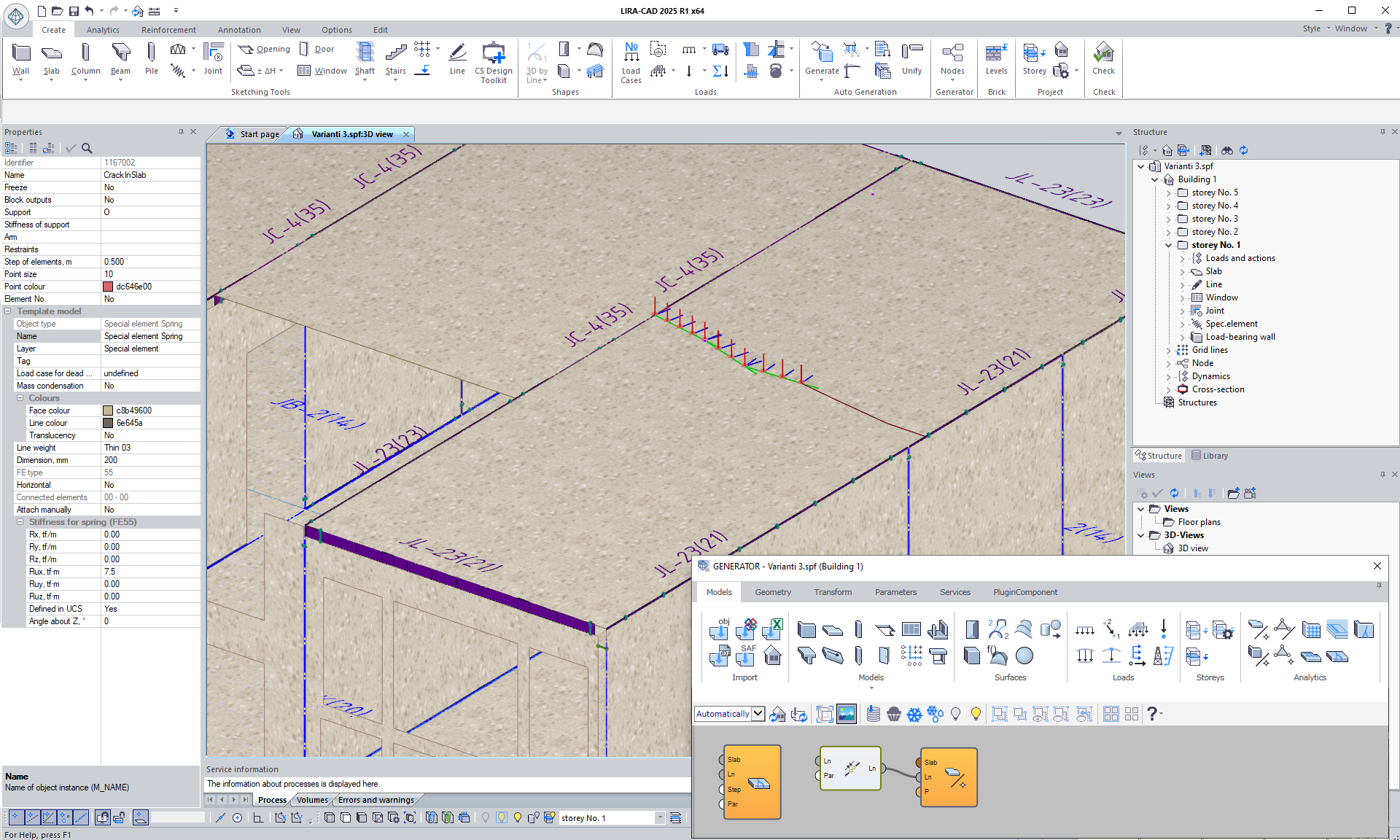
Generator improvements
New nodes are added to the Generator system to extend its functionality:
-
New node Objects in project: stores complete information about all objects in a project, facilitating data management at all stages of design. It allows you to quickly find and select elements by specified criteria such as type, properties or location.
Node 'Objects in Project' - Concentrated load at point: node allows you to specify point loads at specific locations in the structure. The user can define not only the coordinates where the load is applied to, but also define the direction of the load using a vector and define the load value.
-
Generate linear loads by the specified load: this node implements the process of determining the required load intensity and application of loads to objects. The user can specify the line along which the load will be distributed and select the elements, such as bars, that the load will be directed to. For accurate modelling, the direction of load propagation can be adjusted by specifying the appropriate vector.
Once all parameters are defined, the load is visually displayed on the model. So, the user could verify that the load is applied correctly and make any required modifications. - Contour fragmentation: node splits (cuts) a complex closed contour into square contours in which the side is equal to the specified fragmentation step. This tool is especially useful when you need to approximate curved contours for further evaluation or processing.
-
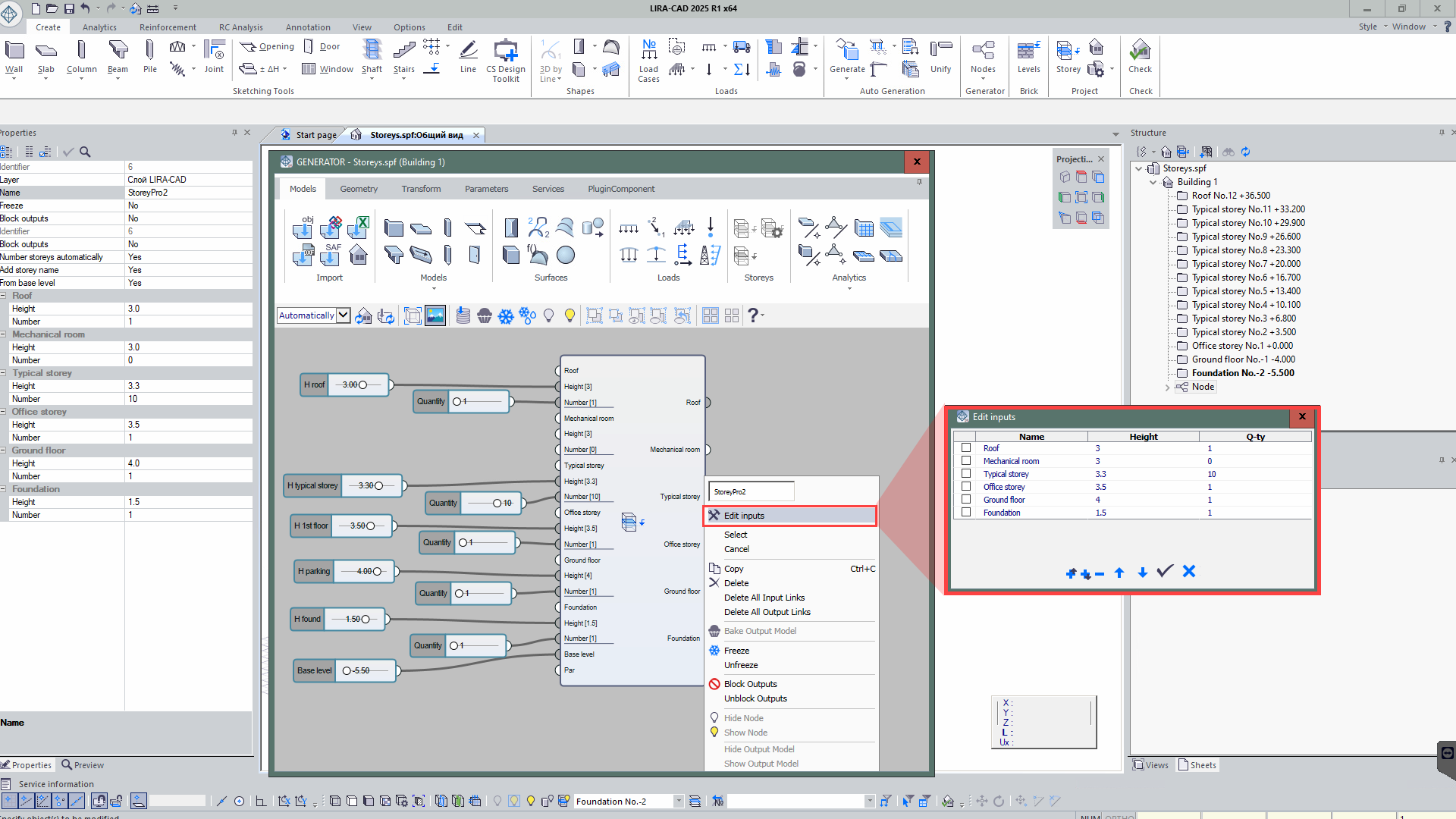
Advanced generation of storeys by height and number: this node provides flexible tools for modelling the storey of a building with account of the height and number of storeys. This feature is very popular with users who have called for its further development. All of this information is now simply contained in a single node, eliminating the need to enter other nodes that were previously used to indicate the number of storeys and their heights.
Node 'Generation of storeys' -
Compute the centre of mass and normal vector of a contour: this node provides the option to compute the centre of mass and normal vector for contours.
Node 'Compute the centre of mass and normal vector of a contour' - Extended functionality of the Block of nodes: now it supports nested blocks, allowing you to place one block inside another.
- Vector product, angle between vectors: this node extends the options in working with vectors, allowing to perform additional mathematical operations. In addition, the option to calculate the angle between vectors allows you to evaluate the relative orientation of elements in space.
- Function graph value: this node is mentioned to calculate function values at specified points based on the provided graph. It allows you to obtain Y values for certain X values based on the specified data. When this node is applied, the user could efficiently obtain function values at arbitrary points; it is especially useful when you need to interpolate or extrapolate between known points.
- Generate segments between all points of array P0 and array P1: this node automates the process of creating segments between sets of points; it allows you to connect each point in array P0 to each point in array P1. This greatly simplifies the generation of complex geometric structures where many points should be connected to each other.
-
New node Tunnel: solves the problem of confusing links in complex models by providing a 'wireless' way to transfer data between elements. Links are created automatically based on matches in key names, simplifying the model structure and making it easier to work with elements that are far apart on the canvas.
Node 'Tunnel' -
New node Multiplexer: optimizes the work with variant models, allowing you to create and manage multiple design options in a single project without duplicating files.
- Fast replacement of design elements: it is easy to replace elements based on the line and the original object.
- Option to modify properties for elements that are of the same type: to work with one type of element, modify its properties in different ways.
- Easy variant management is possible because to the multi-layer technique, which eliminates the need to navigate between files to control and adjust parameters.
-
New nodes Crack in the slab and Crack in the wall: these nodes allow modelling damage/defects in building structures with special FEs. The user can define a line that follows the trajectory of crack propagation. Then adjust the step, stiffnesses, and UCS position for the special FEs to simulate the damage.Node 'Crack in the slab'
- The properties of the node Filter elements of specified layer: a convenient drop-down list with all model layers is now displayed instead of a dialog box. It allows you to select the required layer faster and significantly speeds up the work process.
- In the node of creating piles by points, it is now possible to select any cross-section from the LIRA-CAD library. This improvement allows more accurate modelling of the meshed model and reduces the need for manual editing when some parameters are missing in the nodes.
- In the node DXF/DWG Import files, there is now an option to group and split standard storeys. It allows simplifying and speeding up the input of structural objects if they are the same on standard storeys. When splitting, the flexibility to add structural elements with unique features to the storeys of the same type is preserved while ensuring the convenience and efficiency of working with this node. The underlay by storey mode will also automatically generate storeys based on the number of standard underlays in the file, as well as locate underlays on storeys and align storeys in the plan according to the specified base points.
- In the node Symmetry of objects relative to plane/line, the work algorithms are updated, and the model generation procedures employing its functions are optimized.
DWG export/import improvements
In the LIRA-CAD module, the DWG file import tool is greatly improved. The tool now enables you to generate new objects tailored for the LIRA-CAD module and more precisely modify parameters throughout the import process.
Users praised the previously created technology for importing DWG from a single file. To boost efficiency and convenience, this capability has been substantially enhanced in the latest release.
- Multi-layered drawings for a single storey:
In previous versions, all structural elements were located on one drawing, which occasionally led to crowded data. With the updated version, users can organize the structural components by category and produce many drawings for a single storey. For example:
- Separate drawing for the pile groups and foundation slab.
- Separate drawing for columns and walls.
- Separate drawing for beams and slabs.
- Advantages of the new approach:
This way of entering data makes the process more convenient and reduces the chance of errors. It is simpler to locate and modify the elements you require when they are divided by categories.
- Consistency with familiar design practices:
The new approach is closer to the standard technology of working drawings, where similar elements are displayed on separate sheets. This shortens working time, reduces the risk of errors, and makes the data entry process more intuitive without the need for retraining.
IFC improvements
Importing model to IFC format
The new LIRA-CAD module offers a more flexible and accurate way to define parameters for the work with IFC files. This greatly enhances the import process and data adaptability to project requirements. Users may now configure the correspondence between object parameters in IFC and parameters in the LIRA-CAD module. The settings can be applied individually for each type of objects, ensuring high accuracy of data transfer and correspondence.
Key features and improvements:
-
Import of the model with updating of all structures in the model:
Users can import the model to an existing building and replace the previous structures with the current version; it helps to synchronise the data at different stages of the design.
-
Import of several structures within the one project:
Import of multiple structures within a single project is supported; it simplifies the work with complex models and improves coordination between different design chapters.
-
Improved mechanism for conversion of objects:
An improved algorithm is implemented; it converts general-purpose objects into LIRA-CAD compliant structural elements, speeding up the data integration process.
-
Setting the parameters of materials and sections:
It is possible to specify material and cross-sectional parameters for each group of elements on an element-by-element basis. This provides greater flexibility in modelling and analyses, allowing the design to be adapted to specific requirements.
-
A mechanism to sort and evaluate data in the dialog box:
In the import dialog box now it is possible to sort columns; it makes working with huge amounts of data more convenient and makes data evaluation and correction easier.
-
Option to display the number of elements by groups:
There is a column with the number of elements that belong to certain groups based on materials or sections; it enables the user to quickly assess the scope of the project.
-
Flexible modification of additional parameters:
The import tool increases data transfer accuracy and facilitates collaboration with other project participants by enabling the user to set attributes such as IFC identifier, interpretation, tags, and names.
-
Improved mechanism for generation of storeys:
Updated algorithm for generation of storeys for imported buildings in case there is no information about storeys or slabs located at intermediate elevations between levels. This ensures correct generation of storeys and facilitates further work with the model.
Exporting the model to IFC format
The program exports the model to the IFC format that supports flexible configuration and permits the exported data to be modified in accordance with project specifications.
This tool provides the following options:
- To select the objects to be exported:
- all objects of the model.
- selected objects; it is convenient for transferring only individual parts of the project.
- selected and visible objects with account of the current view of the model on the screen.
-
Checkpoint snap of the building:
When exporting, you can set the exact coordinates of the checkpoint snaps for the building; it ensures correct positioning of the models in the general project and makes integrating with other applications and participants easier.
-
To customize the settings for the export:
The tool enables the user to flexibly select the parameters to be exported for each element. This includes geometric properties, physical properties, materials and other data important for an accurate description of the model.
-
To save the presets of the settings:
The presets for the export settings can be saved for easy reference. So, you could use the preset settings in the subsequent export operation, saving the time and reducing the possibility of configuration errors.
-
User-defined parameters:
The User-defined parameters tool allows the user to create a set of additional parameters that you can control during the process.
These parameters are also transferred to IFC format and can be integrated with other programs, ensuring full data consistency throughout all stages of the design process.
Tekla Structures Plug-in improvements
LIRA-FEM 2025 provides two-way integration with Tekla Structures 2024. The analytical model is exported from Tekla Structures 2024 to LIRA-FEM, while the selected reinforcement and updated finite element cross sections are imported to Tekla Structures 2024 from LIRA-FEM.
Autodesk Revit Plug-in improvements
Autodesk Revit 2025 and LIRA-FEM are integrated via a two-way converter. Thus, there is full data exchange between the programs. As a result, engineers can rapidly transfer and synchronise models, and it is possible to carry out complex analyses and design of metal and reinforced concrete (RC) structures.
Improvements in API and input tables
Expanded options to generate the model and get access to analysis results. Thus, you might use the API to generate your own modules. For example, generate complex objects, automate routine operations, and obtain information on architectural or design models so that the models can be transferred to other software and vice versa.
New input tables are added to define/edit the following data: arc grid lines; types of pilot reinforcement (PR) and their assignment to elements of the model; input data for dynamic load cases; selective consideration of masses in elements; eccentricities of mass application; loads; surface loads; loads on fragment; bar analogues; plate analogues.
Keep in mind that Input Tables can be used as an alternative way to define and edit data about design models, import data from other programs, and partially copy or update the model - through the user interface or programmatically, via COM technology.
Tekla Structures Plug-in improvements
This made it possible for engineers to analyse and design metal and reinforced concrete structures more quickly and effectively by integrating data and models between Tekla Structures 2023 and the LIRA-FEM program.
Generator improvements
-
A new technology for dynamic link with DWG files is introduced. All of the model and storey data may be specified in a single file, which makes it more easier to coordinate the project and make modifications, and it also reduces the possibility of errors when working with several files.
-
To create both main and additional reinforcement zones in floor slabs and foundation slabs, new tools have been developed. So, it will be simpler to move a design option from a 2D drawing to a 3D model of the project.
-
Improved nodes for IFC import are a significant factor that helps make structural items specified in IFC files easier to understand, even when their geometry is distorted.
-
For the nodes, it is possible to define the linear and surface loads in the model. The intensity of these loads vary. Because of this, you can more precisely simulate design models and more accurately describe the actual behaviour of the building.
-
New parameters are introduced for the surface load; triangulation of slabs and walls depends on these parameters.
-
Using pre-defined shapes, such as polylines or underlays, is not the only way to create openings. The perimeters of the current structural elements, such as the beams, slabs, and columns, may also serve as a basis. Using the dimensions and shapes of the existing objects, this approach generates openings more quickly and accurately. This method eliminates the unnecessary step of drawing individual contours for every opening, considerably accelerates the modelling process, and improves design correctness and efficiency.
Rhino (Grasshopper) Plug-in improvements
-
To work in the Rhino 8 (Grasshopper) environment, the LIRA-CAD 2024 plug-in was modified. It allows geometry to be transferred from Grasshopper to the LIRA-CAD module natively. A two-way integration between Rhino 8 (Grasshopper) and the LIRA-CAD module is developed in this version of the program.
Model update improvements
The "feedback" options between the project's design model (VISOR) and analytical model (LIRA-CAD) have been improved. The LIRA-CAD module can now receive updates to cross-sections of elements that were modified in the VISOR module in addition to the results of strength analysis and analysis of reinforcement
If the stress-strain state of the structure is evaluated and it is necessary to relocate columns or modify the cross-sections of certain elements, then such modifications may be transferred from the VISOR module to the LIRA-CAD module with a single click. So the changes will be automatically applied to the LIRA-CAD physical model, which reduces the errors in case the model is updated manually and provides additional time for decision-making and modelling alternatives.
IFC improvements
A major improvement that offers more precise and adaptable parameter settings when importing IFC files is included in the latest release. As a result, users now have the ability to establish more detailed relationships between parameters of an IFC object and parameters of objects in the LIRA-CAD module. Each particular kind of object can have this customization applied; it helps with more precise and customized data import.
The following key changes and improvements should be noted:
-
Parameters of IFC objects: Now, when importing an IFC file, users can customize parameters of the IFC objects so that they correspond to parameters of objects in the LIRA-CAD module. This makes it possible for the two systems to match data more precisely and facilitates a quicker import procedure.
-
Matching for materials and cross-sections: A new option to match materials and cross-sections in elements is added for more in-depth modelling and evaluation. When importing data from IFC, this helps the user determine the element properties more precisely.
-
Assign properties to structural elements: Now you can assign properties to structural elements. Then, such elements are imported to LIRA-CAD either with all properties or with selected ones. This makes it possible to fill the model with the necessary information in LIRA-CAD module.
-
Filters for objects: New functionality enables the user to filter objects based on the parameters used in IFC objects. This makes it easier to find objects that have a certain set of parameters.
-
Export of elements with built-up sections: This feature expands the possibilities for platform and system integration by enabling the export of elements with built-up sections to IFC.
-
Check the model after import: When the building information model is imported and the frame structure is created, a check for possible errors is made for the entire model. The inaccuracies are subsequently corrected in an automated procedure.
These updates make working with IFC files much more accurate and flexible. They also make it easier to integrate IFC with the LIRA-CAD module, which in turn helps to design building structures more precisely and efficiently.
DWG export/import improvements
The tool for import of DWG file is greatly modified in the latest version of LIRA-CAD module, providing a number of new and enhanced features. With the help of this innovative tool, the user can generate new objects unique to LIRA-CAD and more precisely modify settings during the import procedure.
Important aspects in the new version:
-
Import as a block of underlays: Several floor plans can now be included in a single DWG drawing. In order to accomplish this, specify an elevation or list of elevations for each plan and a base point; the plans will be aligned along the height relative to this point. When the data is imported, several floors are generated, and the plans are placed on top of each other.
-
Create new object types: In this version of the program new object types are added, such as main and additional reinforcement in slabs, opening in load, opening in space, thickening in slab and foundation slab, line segment, arc, polyline, and spline. This makes it easy to transform the location of reinforcement in slabs, get drawings in the LIRA-CAD module, and get the reserve factor of a pilot reinforcement (PR).
-
Use hatching as a basis to generate the building objects: You can now import hatchings from DWG files, it enables you to generate more complex structural objects, loads, spaces, and other elements of the framework.
-
Import 3D polylines: Import of 3D polylines is supported; it enables the user to create objects of complex configuration in the model space.
-
Enhanced work with floors: It is now possible to work with each floor independently and define parameters (thickness, section, materials, etc.) for objects on each floor so as to improve flexibility and accuracy of modelling.
-
Save settings to templates: New option to save parameters of objects to templates and save the template to a separate file. This option makes it simpler to share a customised preset data with coworkers, reuse settings, and standardise projects.
-
Model validation: After the import process and when the framework of the structure is generated, the model is validated for possible errors and inaccuracies that may occur during the generation of the building information model.
The LIRA-CAD model is now much more flexible, accurate, and productive thanks to these upgrades, which also greatly enhance the modelling and import procedures. This leads to better and more effective design of engineering structures.
Autodesk Revit Plug-in improvements
The new version of LIRA-SAPR 2024 software provides extended functionality for two-way integration with Autodesk Revit. For engineers and architects, a lot of things have been significantly improved.
Improvements in API and input tables
-
Enhanced automation tools for model generation and access to analysis results.
-
New input tables to define and modify coordinate axes, height elevations, structural blocks, materials for reinforced concrete, composite (steel and reinforced concrete), masonry reinforcing, and steel and aluminium structures are added. New parameters are added to input tables for perfectly rigid bodies, offsets for bars, forces for bars, and subgrade moduli C1 and C2 for plates and bars.