VERSION HISTORY
LIRA-FEM
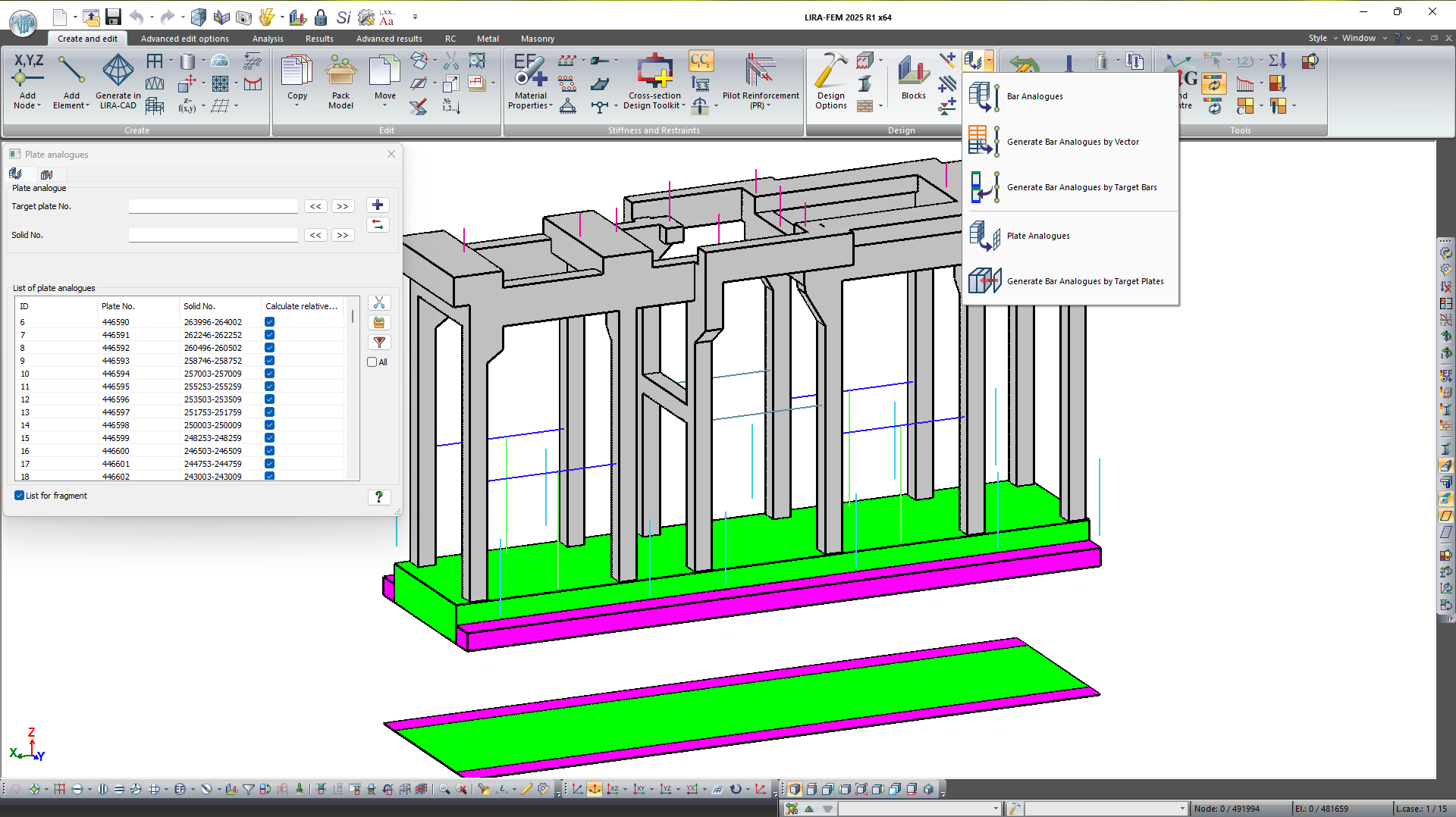
Bar and plate analogues
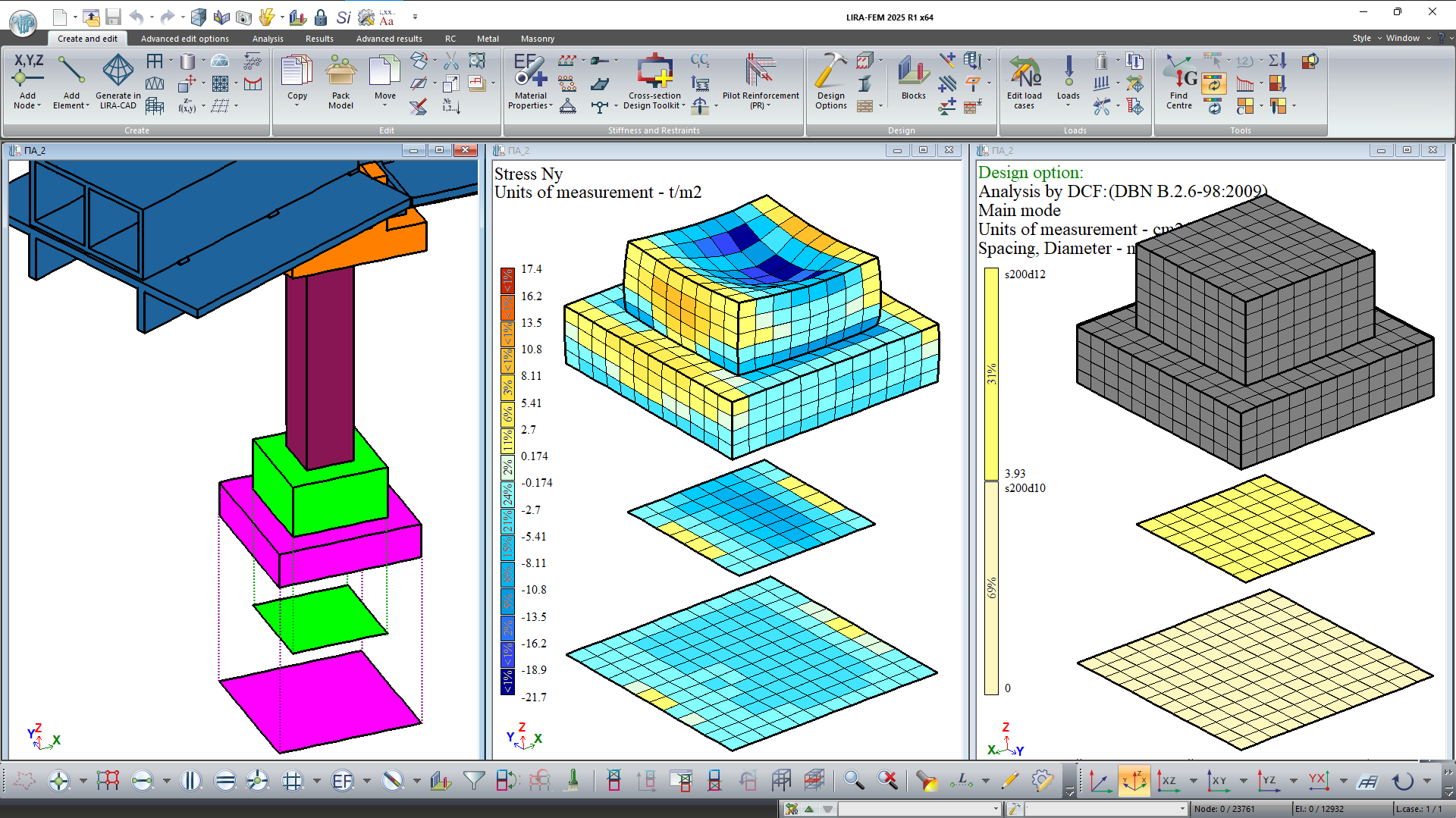
The user can perform analysis of composite structures modelled by a set of 3D elements as plates using the system Plate Analogues.
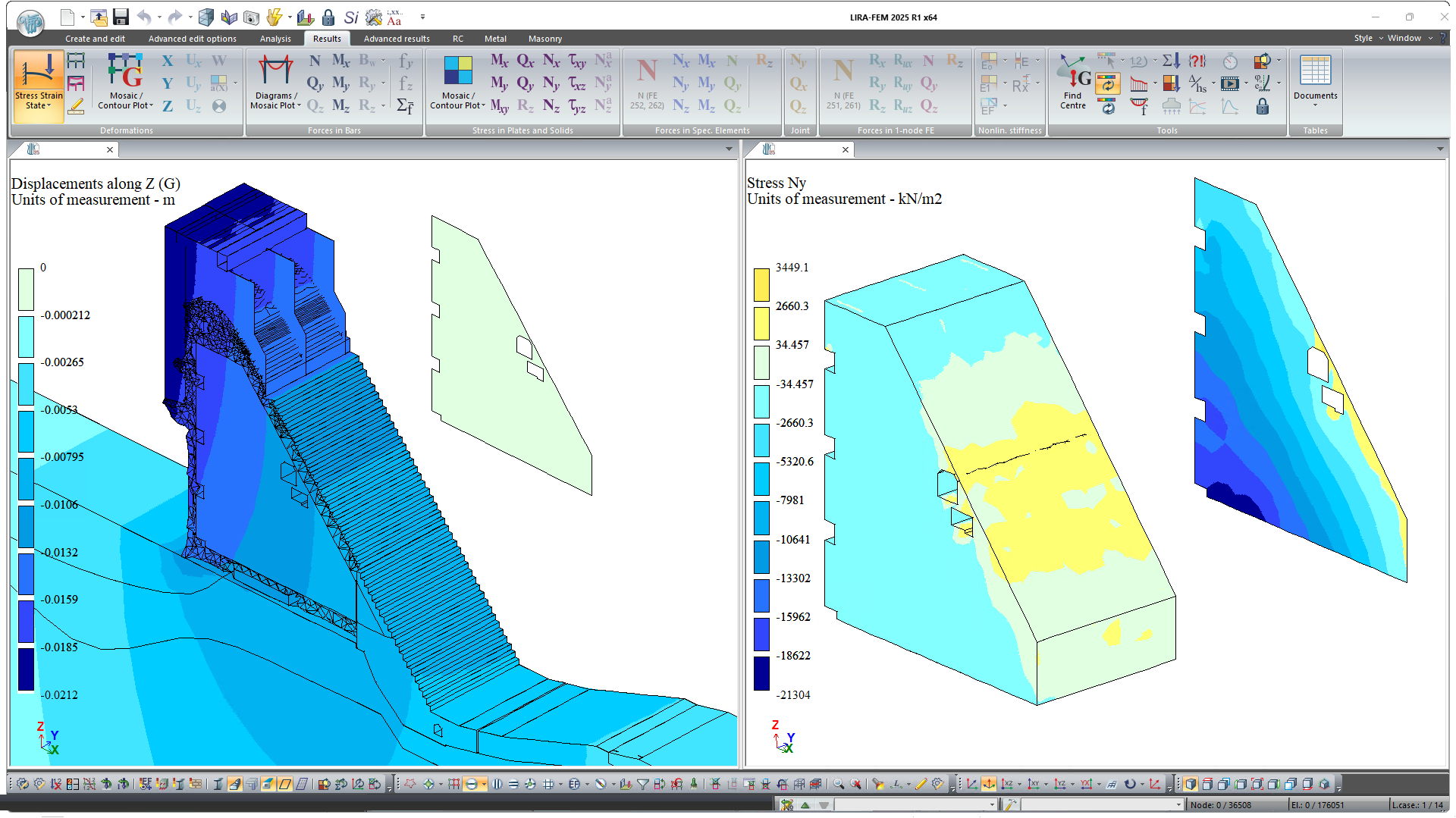
The concept of plate analogues (PA) is that the resulting forces at the centre of the target plate of a PA are calculated from the stresses in the initial 3D elements. PA membrane forces are obtained by integrating normal and tangential stresses over the thickness of the structure; bending moments are obtained by integrating the product of stresses over the corresponding coordinate over the thickness; and shear forces are obtained by integrating tangential stresses over the thickness.
Modelling of engineering objects, such as large thickness foundation slabs, arch vaults, tunnels, multi-layer structures, retaining structures and hydraulic structures (dams, weirs) is often carried out using 3D finite elements. However, this approach can limit the subsequent design stage of these objects. When the Plate Analogues are used for these structures, it is possible to design plate analogues (select and/or check the specified reinforcement in RC elements, check strength in masonry and masonry reinforcing structures, select meshes and longitudinal reinforcement in walls) based on the obtained internal forces in the target plates (PA).