VERSION HISTORY
LIRA-FEM
- Components of BIM technology
- Generating and modifying the model
- Generating and modifying the design model
- Analysis options
- Tools for evaluation of object properties and analysis results
- Analysis & design of reinforced concrete (RC) structures
- RC Expert
- Analysis & design of steel structures
- Soil
- Cross-Section Design Toolkit
- Documentation improvements
Design Model
Generating and modifying the model
- New types of loads have been added:
- Warping at nodes accounts for the inadequacy of the cross-sectional plane of a bar; it is important when for analysis of the thin-walled structures.
- Bimoment at nodes takes into account the moment arising from a force distributed along the height of the cross-section.
- Bimoment by line is mentioned to model a distributed bimoment along an element of the structure.
- Dynamic modules have been added: (22) Impact, (23) Impulse, and (50) Earthquake (AzDTN 2.3-1-2010, modif. on Jan 01, 2014).
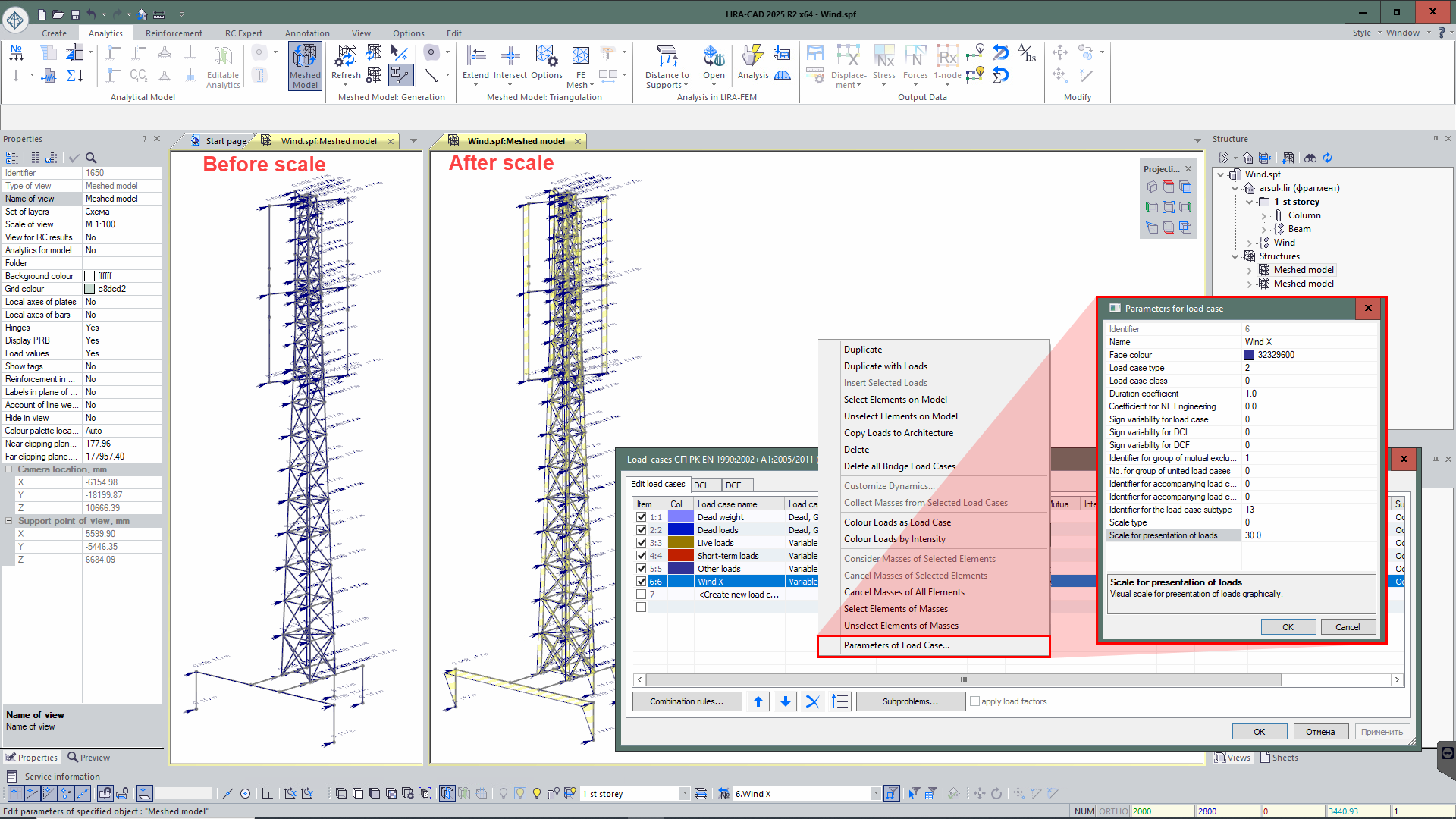
- In the "Parameters for load case" dialog box, the "Scale for presentation of loads" parameter has been added for the selected load. So, it is possible to change the scale of concentrated, linear loads and surface loads, ensuring a more illustrative visualization.
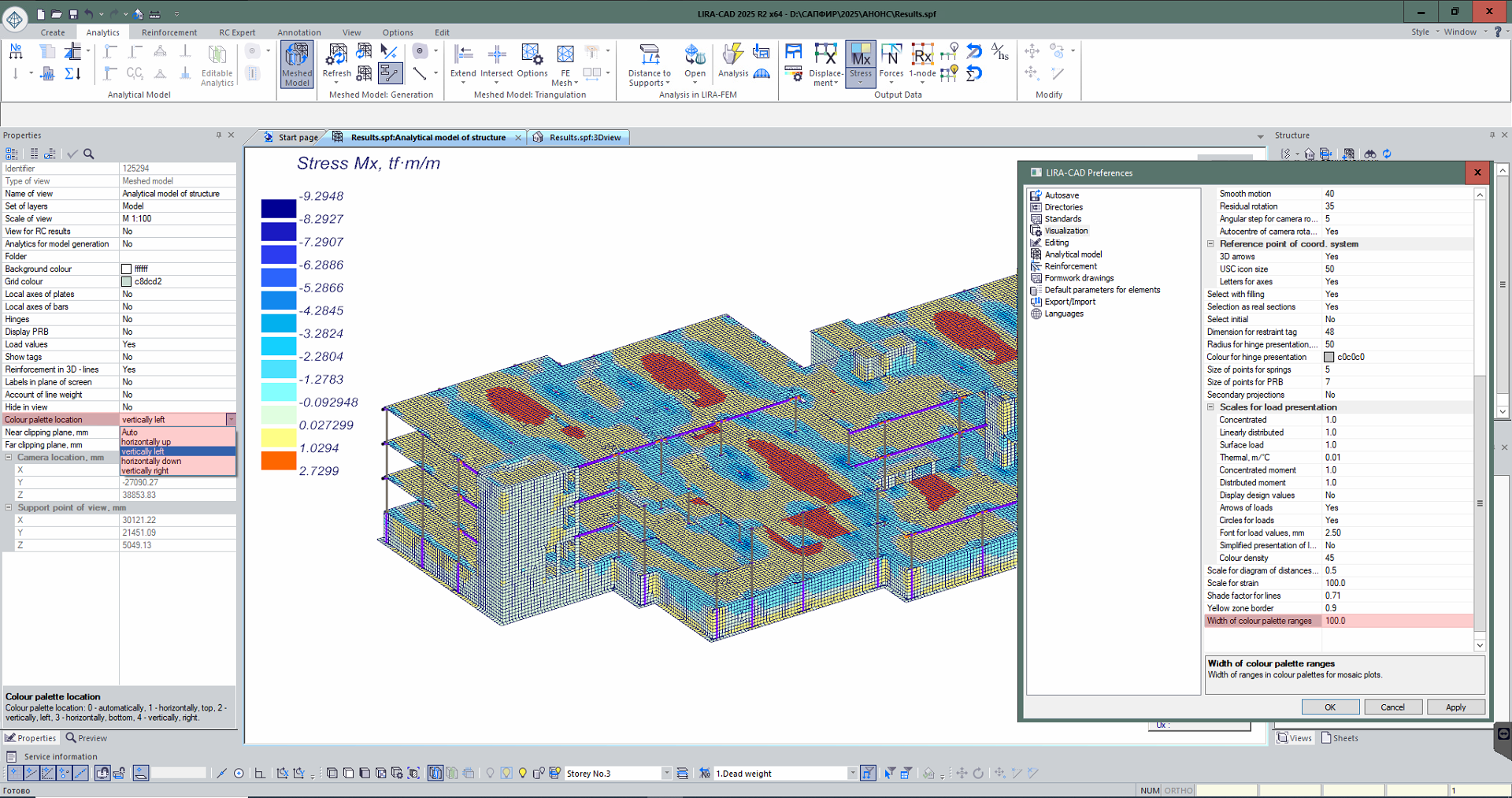
- Location of the colour palette for visualization of analysis results can be customized (in the LIRA-CAD meshed model), including for the visualization of analysis results in the "RC expert" module.
- An option for loads on the staircase has been implemented: to indicate whether the load is included in the additional load case during assemblage.
Additional functionality
Beam
A beam can now be modelled as a bar or plate element. In the new version for beams modelled as plates, it is now possible to specify the design location of the plate - vertical or horizontal. When the analytical representation for the beam is defined as a plate, the Bar Analogue option becomes available.
In the Beam properties dialog box, the parameters for snapping the element relative to the grid line are extended; they include the physical location of the cross-section and the location of the analytical bar. These parameters are now also available in the Filter by parameters and Select by criteria dialog boxes.
Optimised behaviour of the beam in the mode of manual editing of the analytical model; it includes the option to divide the beam into several fragments.
Partitions
R search and L search parameters are added to the object properties. In some cases, when a partition physically rests on a slab, the analytical model representation shows the partition as a linear load and the slab as a plate. If the Align Analytical Model property for the slab is defined as Auto, it can cause that the segments of the analytical plates of slab are shifted to plates of walls or bars of beams. As a result, the load from the partition may not be applied to the slab.
To avoid this case, the added parameters R search and L search ensure that the load is correctly distributed in the described situation and is properly applied to the structural object.
Piles
The program has been updated to provide a manual mode for altering pile models. With this mode, you can shift the pile analytics' location for more precise positioning and separate the pile's analytical bar from its actual volume. This enhances the quality of the FE mesh generation for the beam grillage. It is also possible to consider the influence of the foundation slab's punching shear beneath the pile action.
Grid lines
Previously, if the grid lines belonged to a specific storey and only the current storey was displayed, the grid lines became invisible as they could be on a hidden storey. Now it is possible to enable visualisation of grid lines across the entire building; in this case the grid lines remain linked to their storey. This is particularly useful for IFC import, where the same grid lines may be duplicated on each storey. In LIRA-CAD module, such duplicates can be removed, and thanks to the new setting the grid lines will be correctly displayed in certain views.
Staircase
The weight of the stair treads is now also considered when modelling the load from the dead weight of the structures. This allows for more accurate modelling of the load from these structural elements.
Opening / Door and Window Opening
New options to copy and transfer openings between projects and buildings. For convenient work with openings, their dimensions may be visualized in 3D model. These dimensions are also represented as additional objects that allow you to select the opening when you click on it. This option may be defined in the Filter for object visualization dialog box. It is especially helpful when you work with the model in the top view mode.
Shaft
The main purpose of shaft - is to create openings in slabs that intersect with volume of the shaft. Shafts can be generated either in the physical representation of the model or in the analytical one. In the analytical mode, the shaft contour can be 'magnetized' to analytical plates (walls and slabs), as well as to analytical bars (beams and columns). So, the required openings may be generated more accurately and quickly on several typical storeys at once.
However, the inter-storey staircases are often included in the shaft volume. To ensure that they are correctly represented in the model and are not cut out of the slabs by the shaft, a special property is added to exclude the influence of the shaft on such zones.
Object properties
New tool Additional Properties of Object that allows users to create and manage additional parameters for objects of the model. These parameters provide more detailed control over the model and adapt data to specific project requirements.
The dialog box of this tool displays both custom parameters and standard object properties; it simplifies the data management and provides convenient access to all necessary characteristics in one place.
Linking parameters
The Link parameters of objects function is mentioned to establish a link between similar objects (column, beam, slab, inclined slab, wall, openings in walls, spaces and stairs) based on a selected parameter or group of parameters. The first selected object becomes a base object. It serves as a reference for other objects (followers). Objects may be linked by any parameter available for the selected object, including geometric location, dimensions, material and other parameters. Changes to the parameters of the sample object are automatically applied to all linked follower objects, ensuring data consistency. Additional tools allow you to see by which parameters the objects are linked and visualize the created links in colour. This option reduces the risk of errors and allows you to focus on more complex tasks, trusting routine changes to the software.
Modifying the contours manually
New option to edit manually the contours for Capitals and Column bases. Now it is possible to select capitals or column base as a separate object with its own set of parameters.
Tool: Create by sample
The Create by sample tool allows you to create new objects based on information about existing project elements. This tool greatly simplifies and speeds up the modelling process.
How the tool functions:
For example, if you want to add a column on the 4th storey and a column with the required parameters already exists on the 1st storey, you can select this column and activate the Create by sample command. The program will automatically switch to the mode of creating a structural object with similar properties.
Customization:
Once the command is activated, the user could change any parameters that have been transferred from the selected object. This allows you to minimize data entry and focus only on modifying key parameters.
Benefits:
- Simplify object generation: To add elements quickly based on the elements available in the model.
- Reduced risk of errors: To auto copy parameters; it reduces the incorrect data entry.
- Speeding up the work: To reduce the time required to generate a model.
The Create by sample tool provides accuracy and convenience when creating new elements and duplicating elements; it speeds up the process of model generation.
Tool: Twist angle of the beam section along the trajectory
This tool allows you to model the behaviour of a structure more accurately. The tool takes into account the physics of beam twist along its axis; it is especially important when in analysis of complex 3D structures.
The twist data is not only visually displayed in the model, but is also correctly taken into account when the whole object is divided into finite elements for analysis.
Transfer of project description from LIRA-CAD to LIRA-FEM
In the new version of the program, it is possible to transfer the project description from LIRA-CAD module to LIRA-FEM program. The project description, which is not usually reflected in the project title, can be defined by the user in the project's properties. Now the user could record the data describing the specific features of the object and other important data in LIRA-CAD and transfer it together with the project to LIRA-FEM.
Loads
The following loads can be generated:
- Impulse load at nodes and along the line. For the load, the following data should be defined: load case, load value, load direction, pulse shape, duration of load, period of repetition of the load and number of repetitions of the load. The load may be automatically snapped to the structural object of the building.
- Harmonic load at nodes and along the line. For the load, the following data should be defined: load case, load value, load direction, load diagram, load amplitude, phase shift. The load may be automatically snapped to the structural object of the building. For correct analysis of the dynamic load "Harmonic (24)", a full set of necessary parameters is provided, including the inelastic strength factor of material and the forced frequency of the external action, as well as taking into account the frequencies preceding the specified one.
New types of loads may be created: pyramidal load (property of Surface Load tool) and load from the weight of the coating on the object surface (property of Special Load tool).
It is possible to copy loads from one load case to another, including with a scaling factor. It is also possible to copy load case together with loads. In the Load Editor dialog box, there are options to display loads by area in colours according to their intensity for one or more selected load cases. An option to revert the loads to the load colours is also provided.
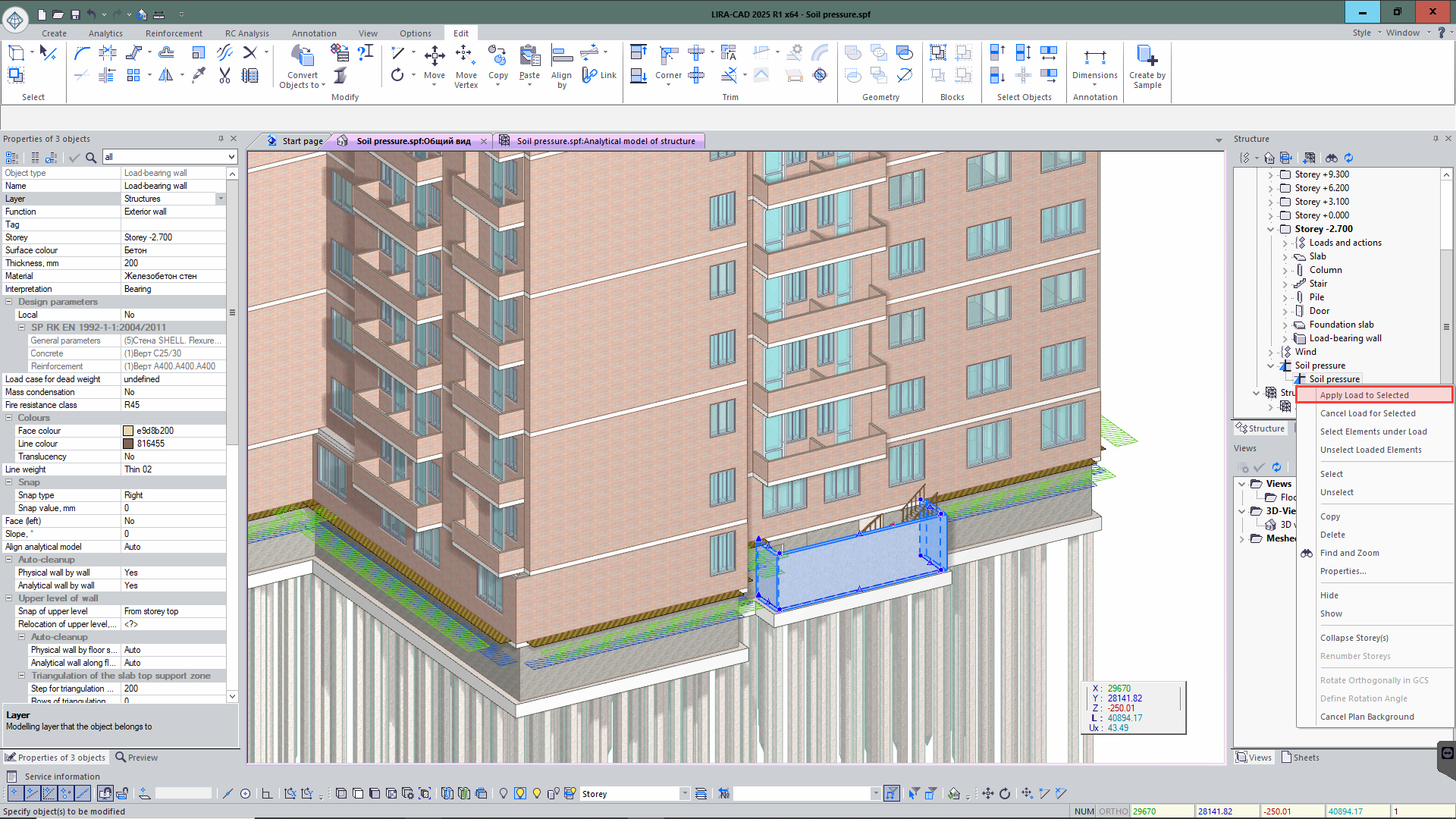
You could manage loads (assign, remove loads and select elements that this load is applied to) from the Project Structure window. It is available for load types: Special Load, Soil Pressure and Ice Load.
Ice load
The tool for collection of ice load is substantially improved:
- Support for building codes: DBN B.1.2 - 2006, NP to SP RK EN 1993-3-1:2006/2011, SNIP 2.01.07-85;
- To collect ise load to the Rope element with account of regulatory documents;
- To collect ise load on structures above 100 metres, with account of regulatory documents;
- To generate the ice wind with account of regulatory documents.
Wind load on the roof
In addition to automatic wind load collection for flat, shed and gable roofs, wind load may be collected from the vaulted roofs in accordance with DBN B.1.2 - 2006 and EN 1991-1-4 is implemented.
Node: Explosion
Node Explosion is mentioned to automate all processes related to the determination of the explosive load intensity and its application to the relevant structural elements, taking into account various explosion parameters (mass of the charge, explosion position (in the air or on the surface), the step for approximation of the overpressure distribution function, the load case No., etc.). Overpressure on structural elements is calculated according to the international standards (UFC 3-340-02: Structures to Resist the Effects of Accidental Explosions). The load can be applied both statically and dynamically. In the latter case, the program automatically generates graphs of the time impact of the impulse.
Note:
When calculating the load intensity, the current version of node does not consder aerodynamic coefficients.
Special load
The Special Load element is mentioned to model pressures of liquids and gases on tank walls, as well as other loads distributed over the area of plate or bar elements. This tool provides realistic modelling and helps the user consider external actions on the structure.
Features and usage:
-
Apply to the elements of the model:
To assign a special load to specific elements or groups of elements, select the Special Load object and the appropriate elements of the model.
-
Multi-level arrangement:
The special load is added to the level of the active project, so it may be applied to elements located on different storeys of the model. This simplifies work with loads in complex projects where elements are distributed on several levels.
-
Generate elementary loads:
When creating a meshed model, each Special Load is converted into a set of elementary loads. The parameters and method of application of these elementary loads depend on the settings for the Special Load object.
-
Verify visually in analytical view:
The distributed loads can be visually verified in advance in the analytical representation of the model; it enables the engineer to confirm that their application is proper prior to analysis.
The use of Special Loads in the LIRA-CAD module makes it possible to effectively take into account complex loads on the structure, ensuring high accuracy of modelling and analyses.
Space load
In the Space contour tool, with the Interpretation option indicated as the Load, it is now possible to apply loads to the following objects: inclined slabs, slabs with variable thickness and stairs.
Moreover, in the new version for this element, there is an additional set of checkpoints displayed at the top of the space. This greatly simplifies and speeds up the process of modifying the space contour.
Auto snap the load to the element
The new version of the program introduces the Load Snap option that allows you to automatically snap a load to a structural element. Before placing the load in the model, the user can activate the Snap command and then select the structural element to which the load will be attached. Then the load attached to the certain object is generated.
Example:
If you design a metal frame where the purlins are supported by main beams, the roof weight can be defined as a linear load along the purlins. If the step of the purlins is changed, the appropriate load will automatically update its location to match the new location of the elements.
Benefits:
- Accuracy and reliability: The load is always linked to the relevant structural element.
- Auto update: When the layout of the elements changes, the load adapts automatically without the need for manual modification.
- Simplifying the modelling process: The function reduces the probability of errors and ensures that the model is generated correctly.
This feature improves the usability and accuracy of the design procedure by automating the work with loads and minimising the risk of errors in case of modification in structure.
Load cases (dialog box)
The following options are added:
- to generate data for subproblems, collect masses, and perform stability analysis;
-
to perform a number of operations via the shortcut menu, including:
- to define dynamic loads (mass collection);
- to colour loads by colours of load cases;
- to colour loads according to their intensity;
- to define parameters for load cases;
- to copy loads from one load case to another.
Analytical model
Subproblems
New technology to define the input data for the Subproblem method. With this technology, many independent sets of subgrade moduli and sets of coefficients to modulus of elasticity can be used in a single design model.
Each loading stage may have a different set of parameters based on the subgrade's properties or maintenance conditions. Therefore, the soil's heterogeneity and the unique features of the foundation-structure interaction may be taken into account; this allows for a more realistic description of the system's actual conditions.
Furthermore, the flexibility to assign different coefficients to the modulus of elasticity at every stage of analysis creates additional opportunities for more precise design solutions.
Input data for the stability analysis
In the new version of LIRA-CAD module, it is possible to define the input data for stability analysis of structures. Users can define key parameters and select objects for analysis. Main options:
- To select the calculation method: by forces or by DCLs.
- To define load cases: either loads or DCLs to be considered in the analysis procedure.
- To include elements in the analysis: in the properties of objects you could define whether they are considered in stability analysis.
The defined parameters are automatically transferred to LIRA-FEM. So, it eliminates the re-entry of data, reducing the risk of errors and speeding up the modelling and analysis process.
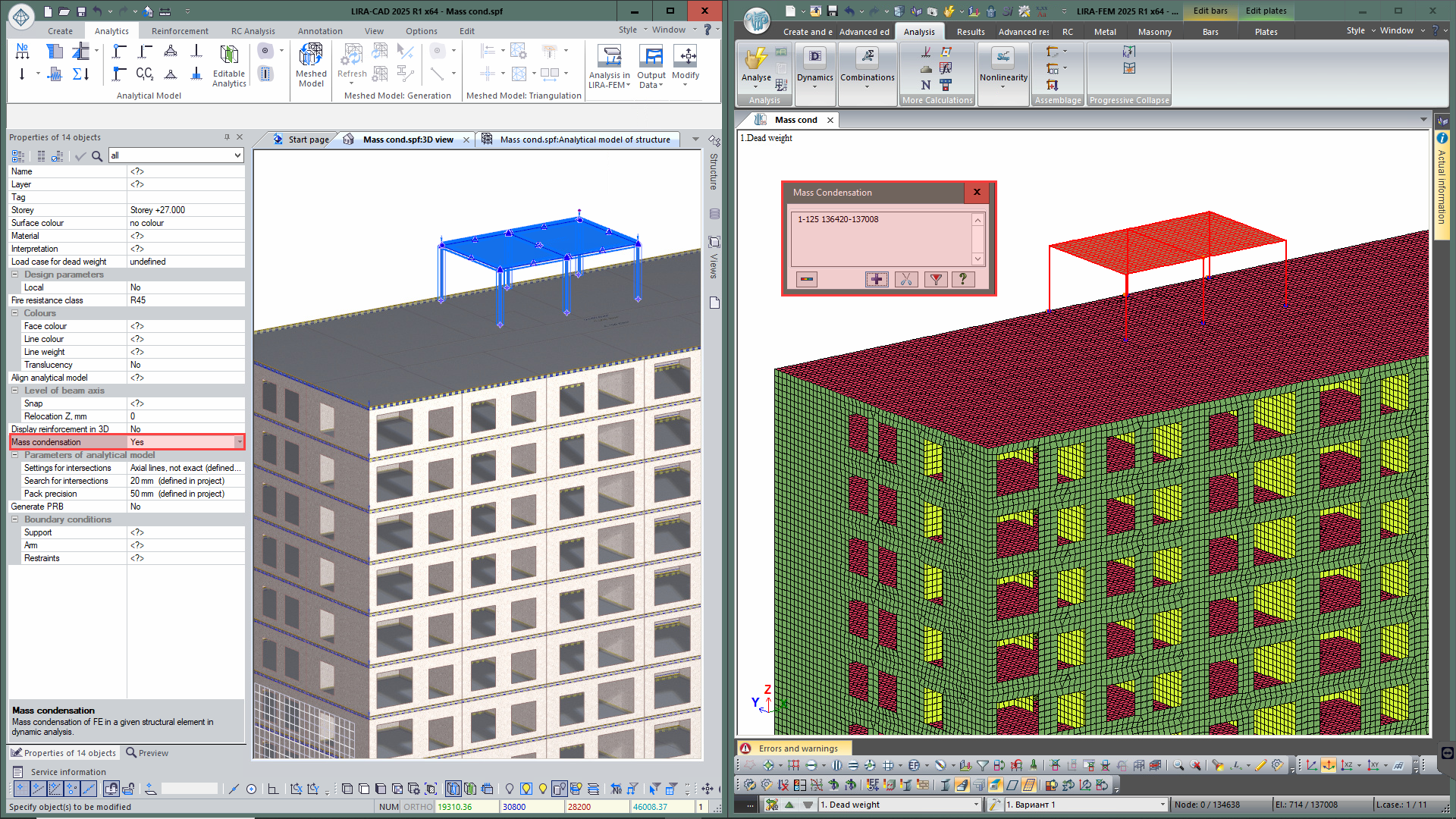
Condensation of masses
New option to define the Condensation of masses to optimise dynamic analyses, especially when analysing vibrations of structures. Only masses of the main structure are considered when searching for mode shapes, while the masses from the flexible part (masses of selected elements in which natural vibrations are not of interest to the user in this problem) are concentrated in its support nodes (support nodes of selected elements). Also, it is now possible to perform Selective account of masses in elements to consider exactly the masses of selected elements for dynamic analysis.
Unification of bars
New option to preliminary unify bar elements (beams and columns) for analysis of reinforcement or metal sections. In the Unify bars dialog box, all elements of the model are listed: columns, beams, as well as elements of trusses and beam systems. The table contains data about name of the element, its length, section and material. Unification can be performed on the basis of tags assigned to elements, or unified groups of structural elements (UGSTE) can be created. A graphic presentation of elements by tag colours is available now. Unified groups (created on the basis of tags or assigned to UGSTEs) can be transferred to the VISOR module of the LIRA-FEM program.
The unification table in its current state can be placed on the drawing as an editable table. You can also export its contents in TXT or CSV formats for Microsoft Excel.
Perfectly rigid bodies (PRB)
In previous versions of the program, there was an option to arrange the combined behaviour of beams and slabs with the Offsets tool that provides a reliable connection between elements. In the new version, an additional option - Perfectly rigid bodies - is added, providing an alternative modelling strategy.
The length of the PRB is determined automatically based on the distance between the analytical models of objects and is updated in real time when any of them is moved. In the analytical representation mode, the PRB model more clearly demonstrates the interaction between the slab (plate) and the beam (bar).
With this approach, the interaction between beams and slabs can be described more precisely and adaptably, ensuring that they behave together as a single system. The use of Perfectly Rigid Bodies extends the functionality of the program, offering a new way of modelling such connections and increasing the accuracy of calculations.
Triangulation
Triangulation regions in the slab above the walls are updated when the walls are moved or modified. New option to update the dimensions of an existing triangulation zone and the step of approximation of its contour lines. In previous versions, it was necessary to delete the old triangulation zone and create a new one with updated parameters.
Triangulation points in the slab above/below the walls are created automatically for flexible customization of triangulation mesh. To manage the triangulation points, use the following parameters: step of triangulation points and number of rows. You can also specify the number of rows with fixed step of triangulation points. In this case the remaining rows will have a transitional step of triangulation points. The value of this transitional step can be in the range from fixed step to user-defined step of triangulation in the plate.
Additional grid of triangulation lines
To improve the accuracy in modelling of slab triangulation zones, a new tool Additional grid of triangulation lines is introduced. It allows the user to define the cells by which the slab is divided into finite elements, providing more detailed modelling.
Key options:
- To define parameters for the cell: The user specifies the dimensions of the cells to be used for triangulation.
- To select the triangulation zone: Define the slab on which the additional grid will be created.
- To define the generation method: Depending on the needs of the project, you can select different shapes for the additional zone: rectangle, sloping rectangle, inscribed or circumscribed polygon.
- To locate the additional zone: The tool allows you to place triangulation zones at key locations to create a denser and more accurate FE mesh.
Benefits:
- Easy to set up and use: The tool is intuitive and easy to set up.
- Visual clarity: The user can immediately see how the future triangulation mesh will look like.
- Modelling accuracy: Provides optimal densification of finite elements in important zones of the meshed model, improving the quality and accuracy of the analysis.
This tool simplifies the creation of complex meshes and allows for precise control of the finite element structure, especially in critical parts of the model.
The Pit
A new object - a Lift Pit is automatically created on the basis of an opening defined in the foundation slab, and its dimensions depend on the dimensions of this opening.
The pit has a set of Slab and Wall parameters that can be modified parametrically (thickness, boundary conditions, interpretation, etc.). For the walls of the pit, it is possible to define a thickness variable in height.
To select the analytical representation of the pit walls, use the parameter Create walls - Yes/No:
- Create walls - Yes - the walls and the slab have an analytical representation of the Plate;
- Create walls - No - the plate has an analytical representation Plate, the walls are replaced with an Offset.
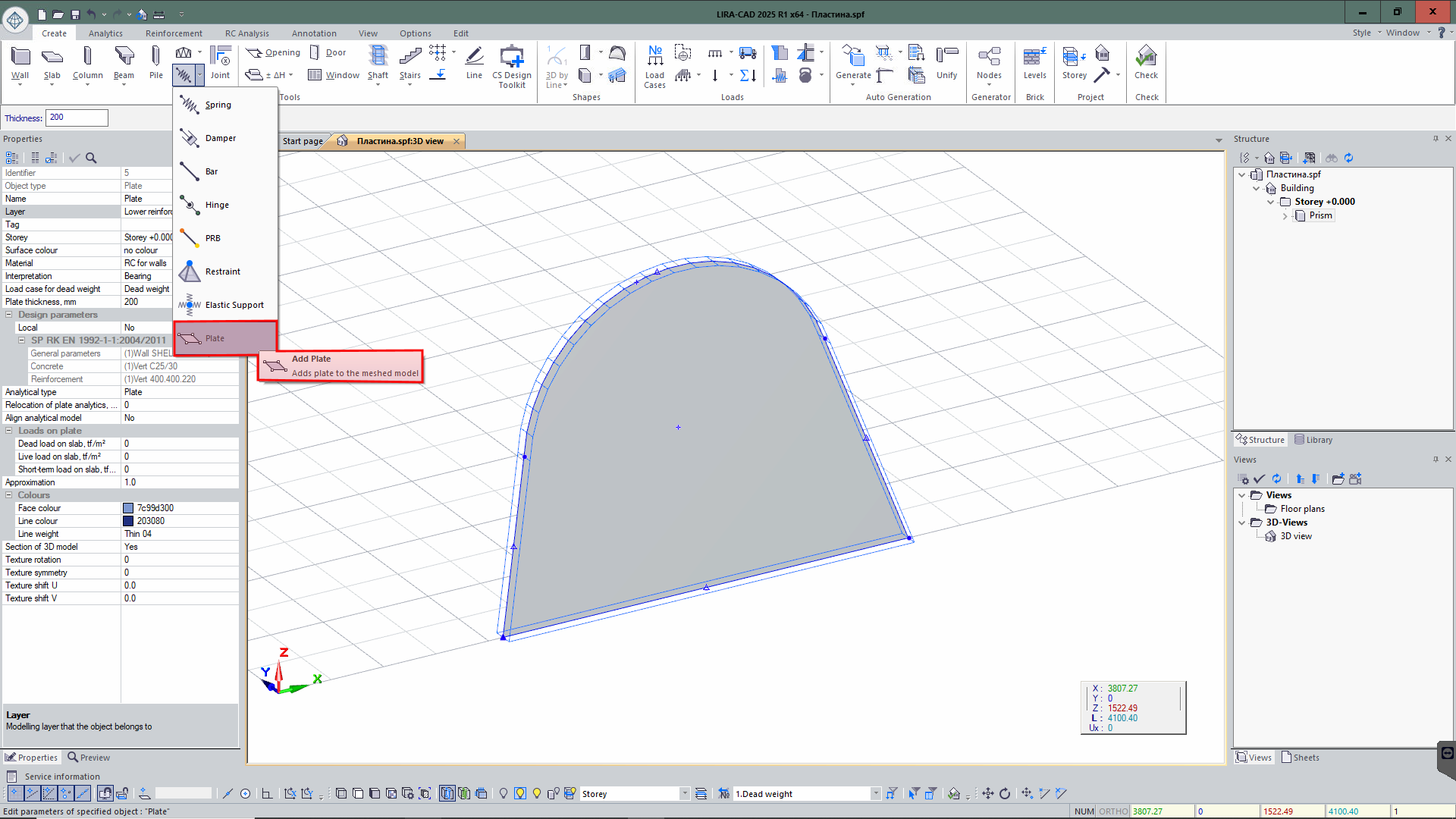
The Plate tool
In addition to the already available special elements such as Free Spring, Damper and Bar, a new tool is added - Plate. This element has all the standard properties of the Slab type element, but its functionality offers a more flexible approach to introducing flat elements into the model.
The Plate tool allows you to generate elements that can be 'magnetized' to the checkpoints of other objects in any way. This generation method greatly simplifies the process of integrating an element into complex structures and offers more precise location in the model. With the help of this tool's versatility and user-friendliness, engineers may effectively build complicated systems by taking into consideration the geometric and structural properties of other elements in the model.
Cable-stayed structures
There is now technology to define the input data for modelling of cable-stayed structures. With this technology, a unique product called Rope can be created. For this element, it is possible to define key parameters necessary for accurate modelling of such structures:
- Type of section , with the rope profile indicated;
- A method for dividing an element to consider its geometric and design properties;
- The tension; so, the stress in the structure will be considered properly.
For complicated cable-stayed systems, including stadiums, roofs, bridges, and other structures with tension elements, this component offers more precise and effective modelling. With this method, the modelling of objects with unusual features is optimised and the accuracy of design solutions is increased.
The Project Template
The Project Template tool is mentioned to simplify the creation and management of projects (documents). Users can create templates either on the basis of existing projects or from scratch, adapting them to specific tasks and requirements.
Project Template options:
-
To preserve the project structure:
The template captures the structure of the project, including the storeys and all the elements placed on storeys; it allows you to quickly reproduce certain configuration.
-
To customize the project parameters:
The template stores key parameters required for the design, such as the applied building code and settings for the meshed model.
-
Load Editor:
The template includes preset load cases and their settings, DCF and DCL parameters; so, it is possible to avoid repeated data entry and improve efficiency.
-
A variety of templates for different tasks:
Templates can be customized for different types of projects, such as metal or reinforced concrete frames, including parameters for creating the PRB, element connections, triangulation step and other parameters that should be considered when modelling a building.
-
To adapt the templates for the building codes:
It is possible to create templates for analyses by different building codes, while keeping all the necessary parameters.
-
Default template:
The user can assign a template that will be automatically applied to all new projects; it speeds up work and minimises errors at the start of the project.
Advantages of templates:
The unlimited number of templates allows the user to customize the templates for different requirements. It speeds up the generation of models, reduces errors and eliminates repetitive data entry. This approach makes the design process more efficient and accurate, especially when you work with typical projects.
Updated graphics engine
The graphics engine in LIRA-CAD 2025 has been updated to support OpenGL 4.6 graphics. It allows for greater compatibility with graphic equipment from various manufacturers and enhances visualization of designed objects.
- The speed for model rendering is increased. Now when you change the view, rotate or perform other actions with the model, the screen refreshes 7-10 times faster compared to previous versions.
- The quality of textures, labels, texts and lines is improved.
- Visual effects of falling shadows, relief surfaces, fog and diffuse shading are implemented.