RC Expert
Reinforced Concrete Expertise is a LIRA-FEM system designed to perform checks of reinforced concrete structures for strength, serviceability, and detailing requirements. The system provides an additional analysis technology for reinforced concrete structures, operating in parallel with the existing tools in LIRA-FEM and LIRA-CAD, and is aimed at meeting the needs of a wide range of users, including designers, experts, and researchers.
Reinforced Concrete Expertise
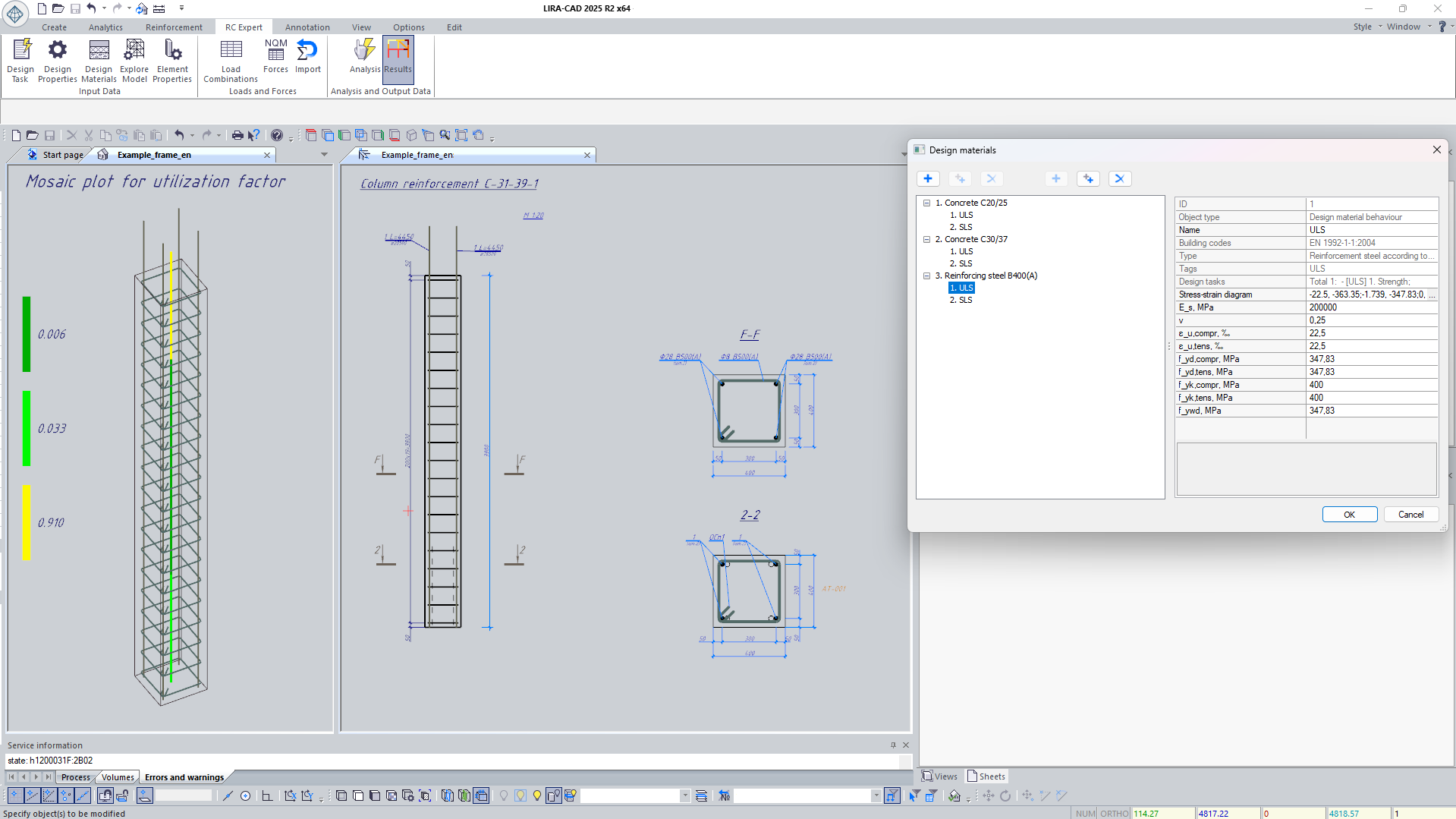
Arbitrary reinforcement layout and the system purpose
An arbitrary reinforcement layout implies not only flexible spatial positioning, but also the ability to assign different design properties to individual reinforcing bars or groups - for cases involving defects, corrosion, strengthening during rehabilitation, the use of composite reinforcement, and similar scenarios.
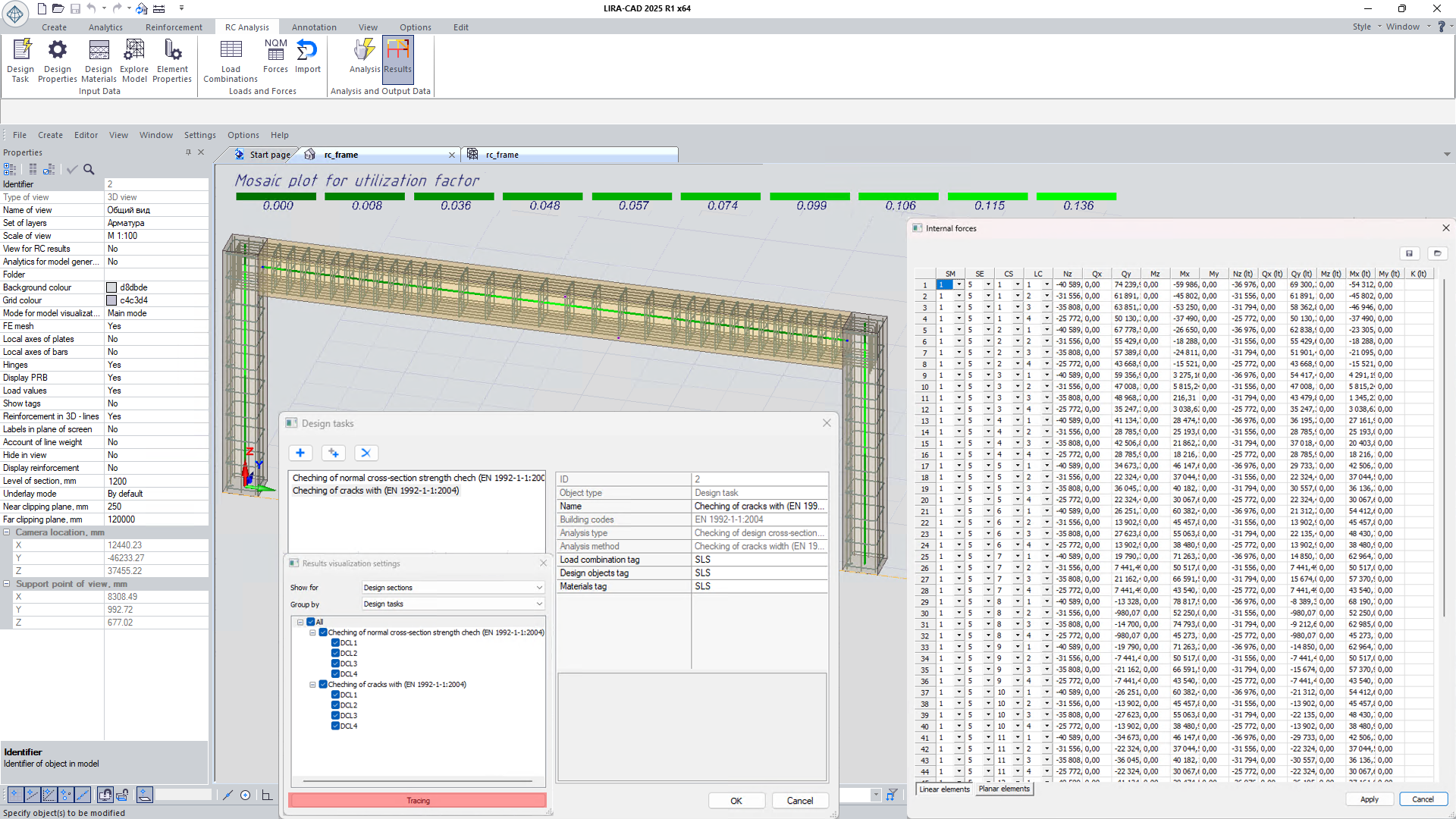
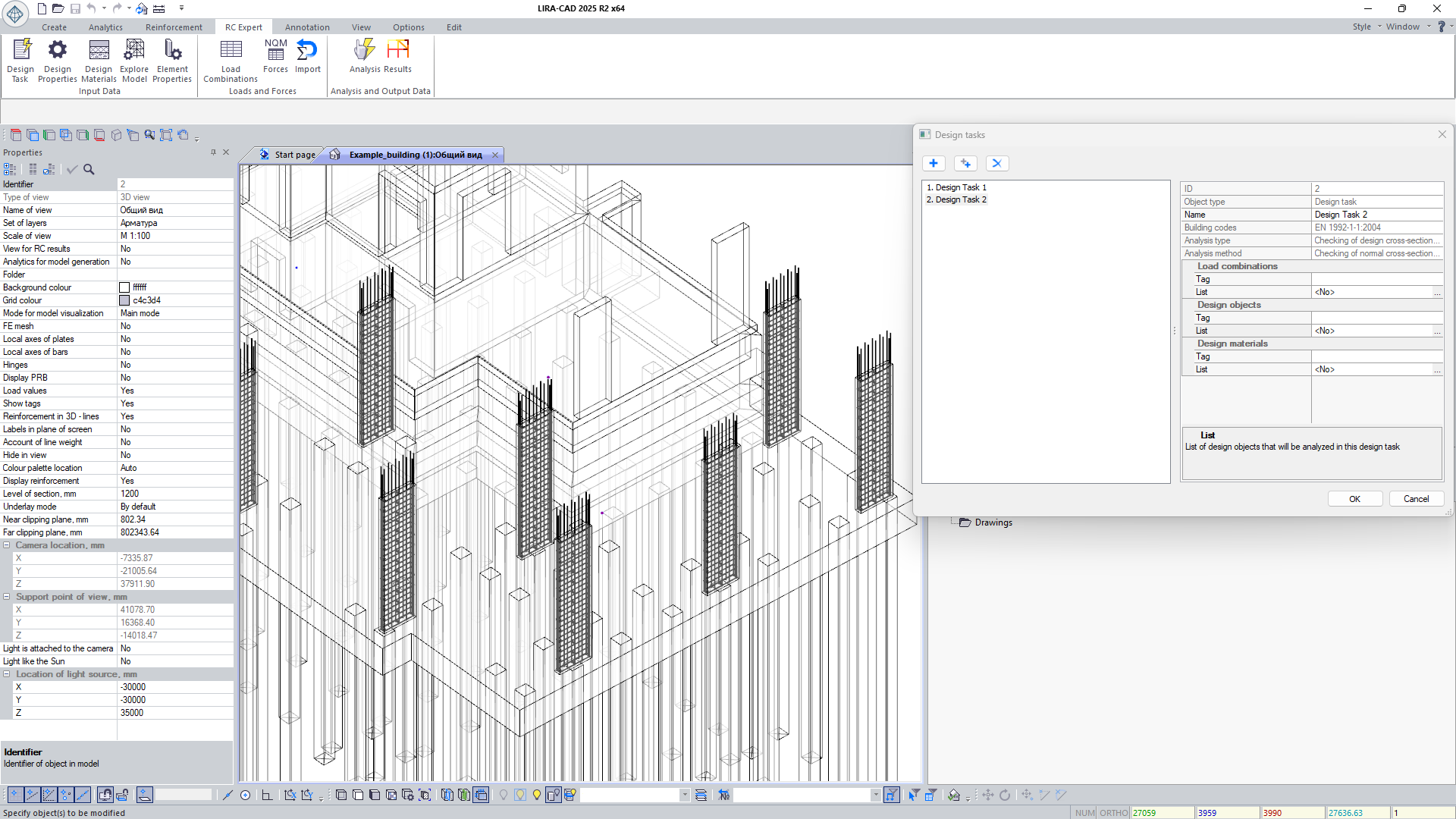
Calculation process setup
- Select the set and order of checks, configure procedures, and account for optional code provisions.
- Select elements to be checked and choose the active load combinations for each check.
- Override structural parameters and coefficients with user-defined values to control the calculation process.
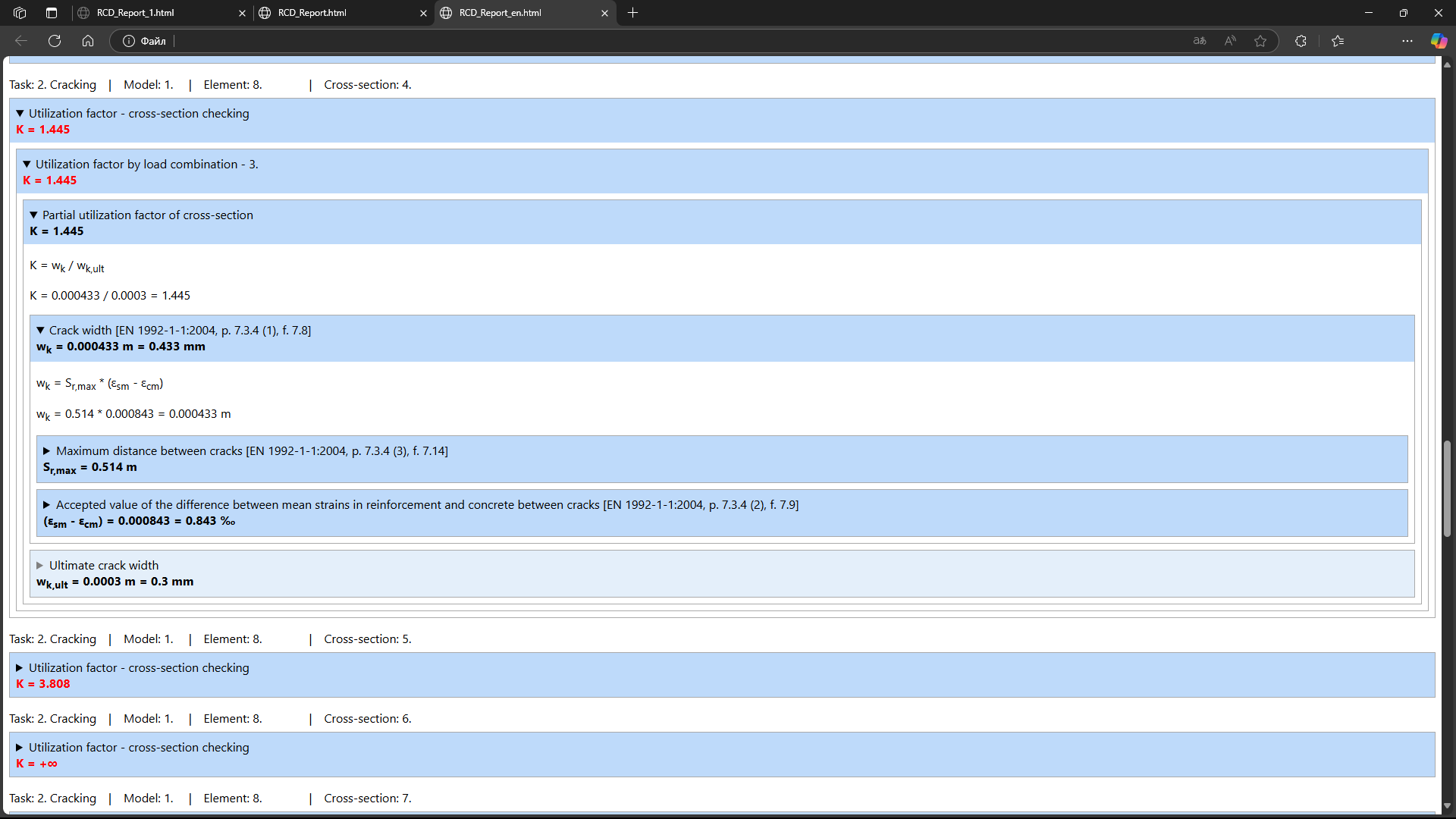
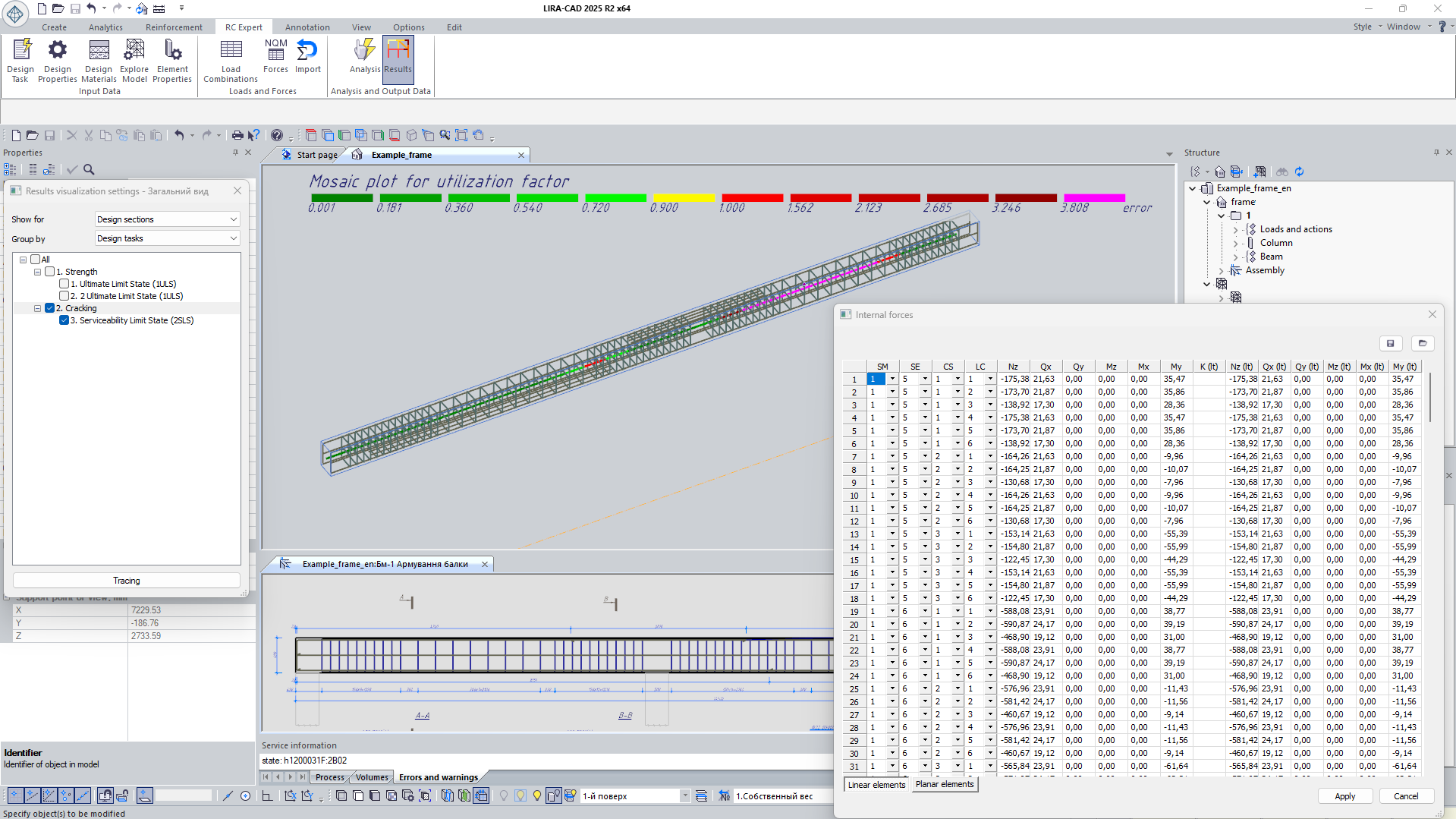
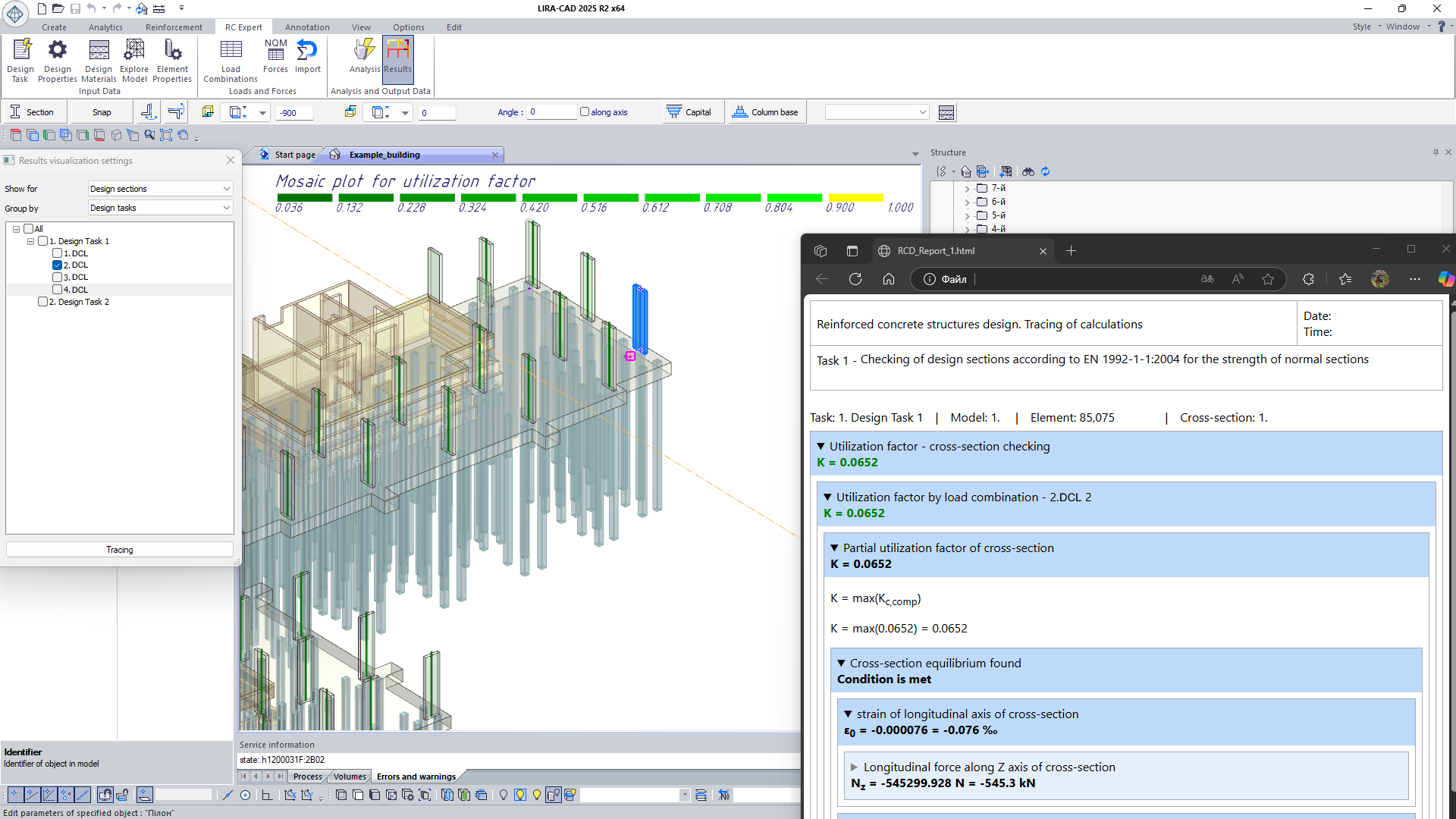
Calculation tracing (HTML report)
For in-depth analysis of results, calculation tracing is used: by following the tree of intermediate values, the process of obtaining the result from the input data can be traced, with the applied calculation formulas displayed. In a web browser, the report is interactive-clicking on a value reveals the formula and the list of related parameters down to the value of interest.
Transparency of calculation procedures
is ensured by detailed explanations of the methods and assumptions used in the computations. These explanations are integrated directly into the user interface and the help system, enabling you to verify and interpret results without referring to external sources.
Implemented checks in LIRA-CAD 2025 R2
- Check of normal cross-sections under axial force and bending moments using a nonlinear deformation model.
- Crack resistance check of normal cross-sections.
- For walls and slabs: normal cross-section strength and crack resistance checks per DBN and EN 1992-1-1.
Evaluate the software
If you have any doubt, download the Demo version and evaluate the program or contact our Support Team for more details.