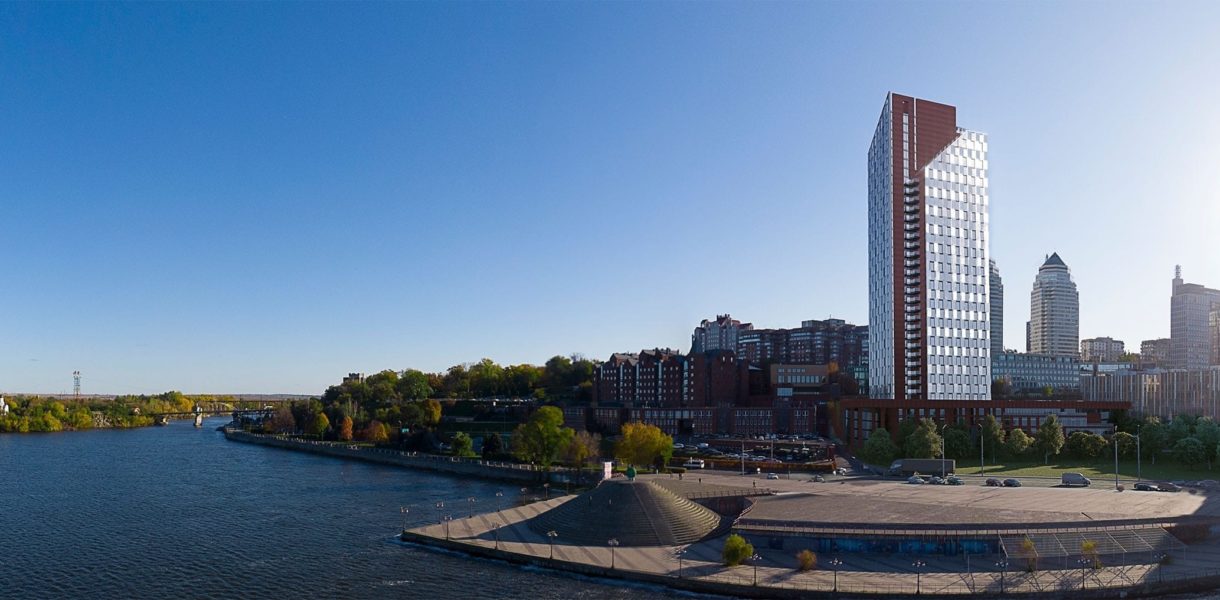
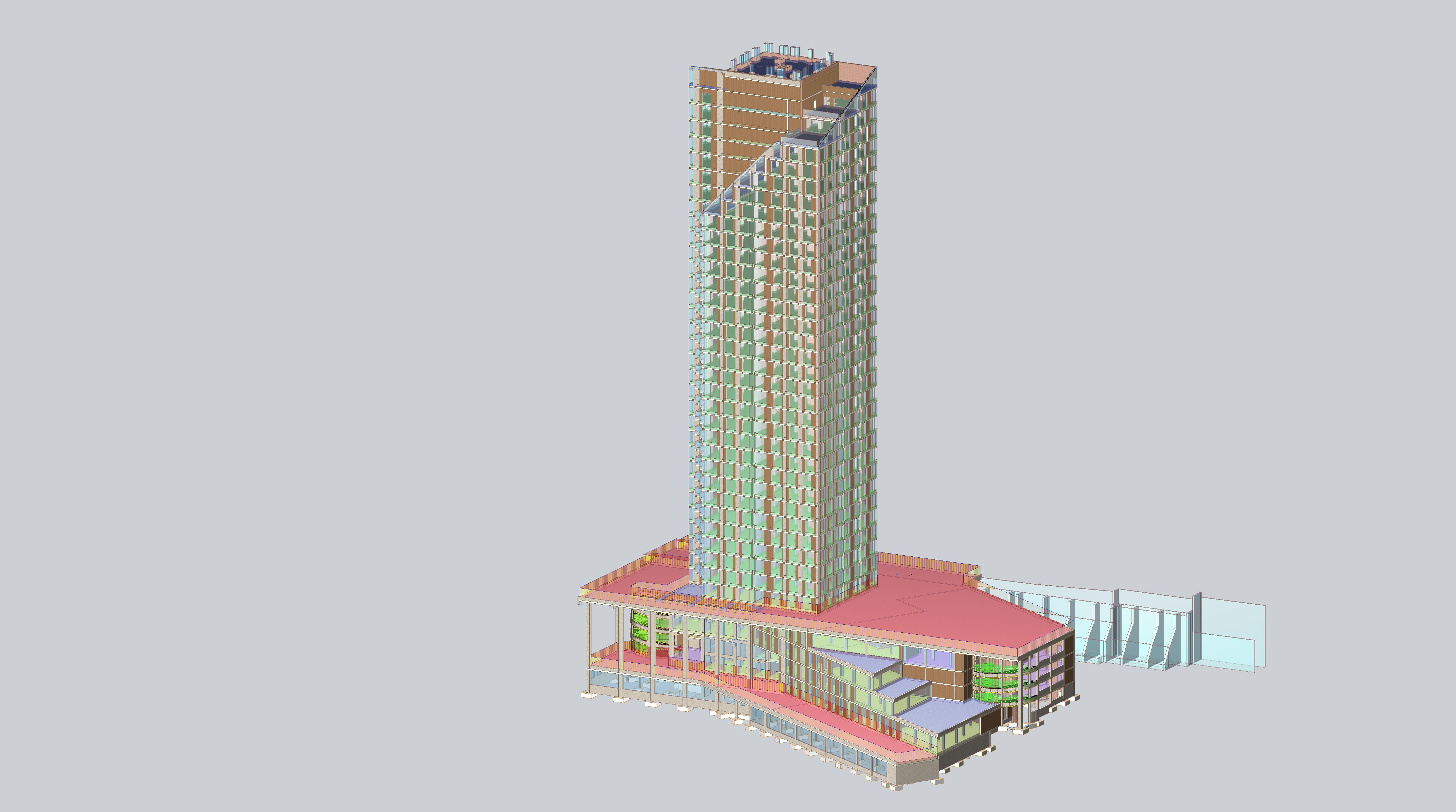
BIM technology for design of a high-rise building
The design model was generated in SAPFIR-3D 2020. BIM model was imported from Revit through the IFC format.

Architectural bureau "Alur", Ukraine
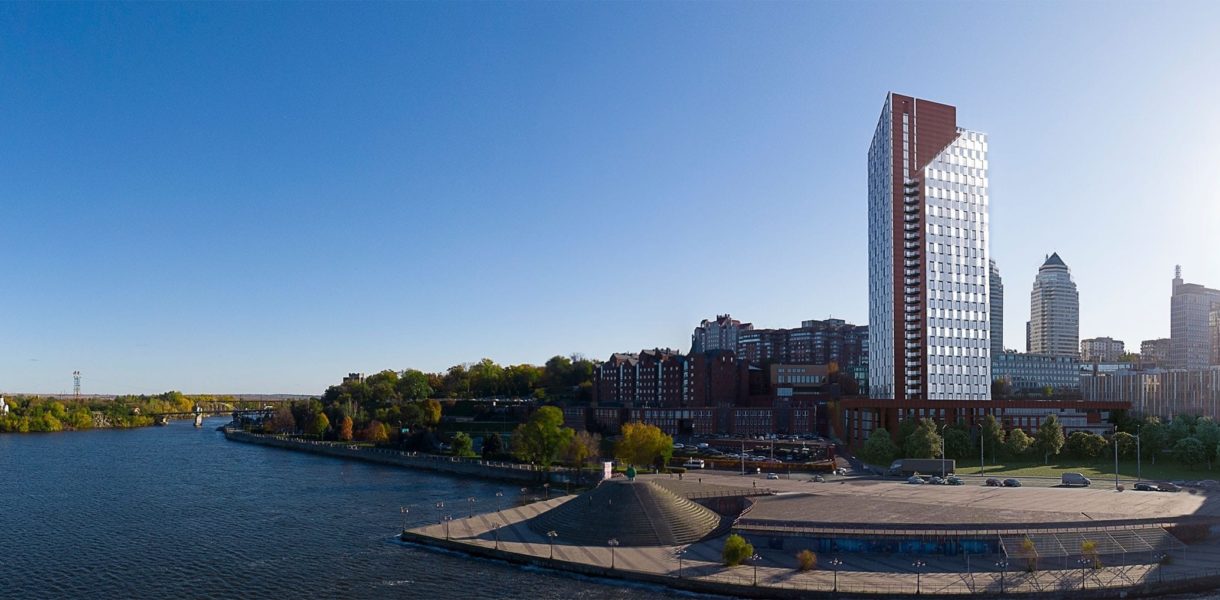
Location: Dnipro city, Ukraine
Engineers
- Architectural bureau "Alur"
- Chief Architect of the project: Leonid Tokarev
- Chief Designer of the project: Alexey Gorchakov
- Architects: Artem Shelipov, Evgenia Chmir, Stanislav Malyukov
- Structural engineers: Vladyslav Sydoruk, Oleg Robkin
- Author of the design model: Alexey Gorchakov
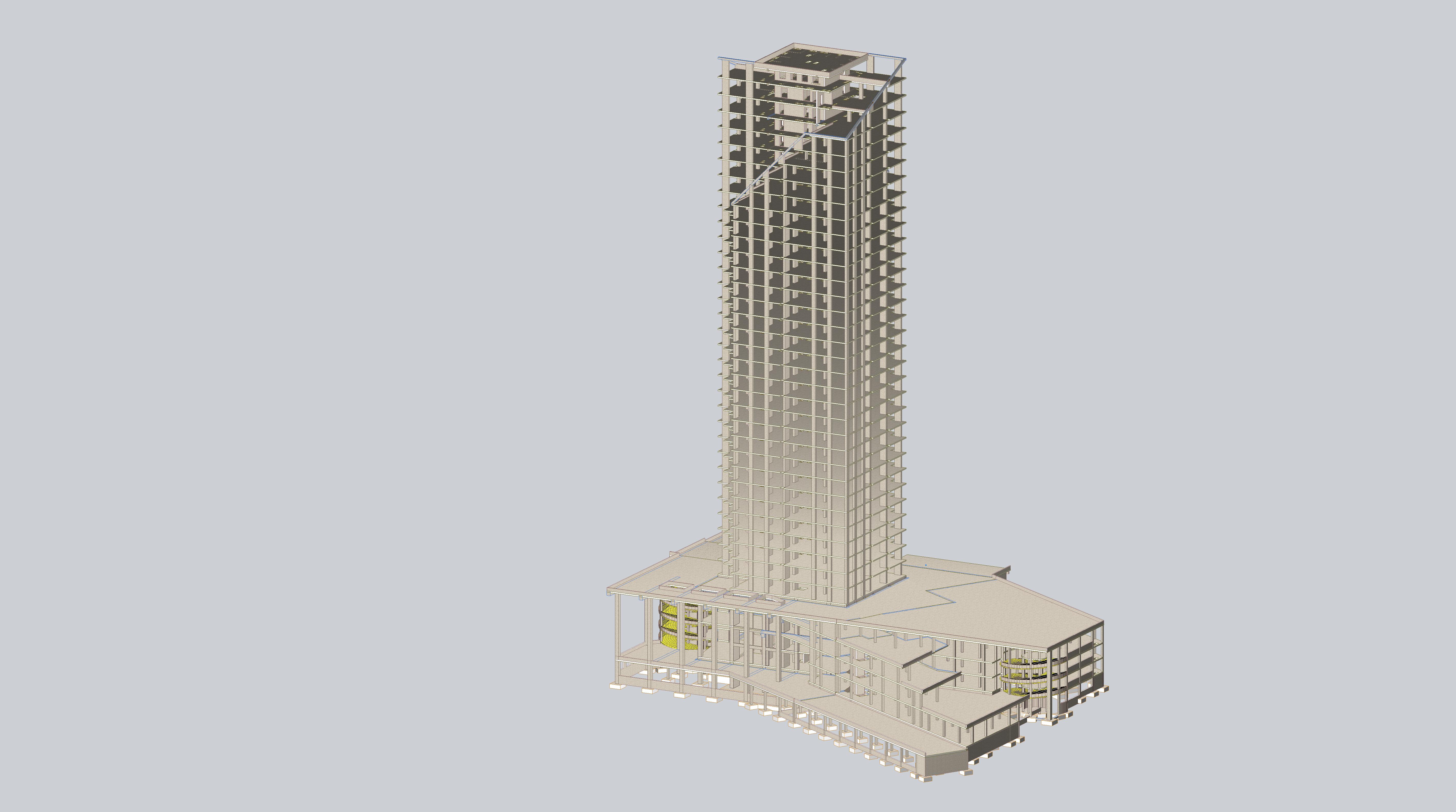
Design model
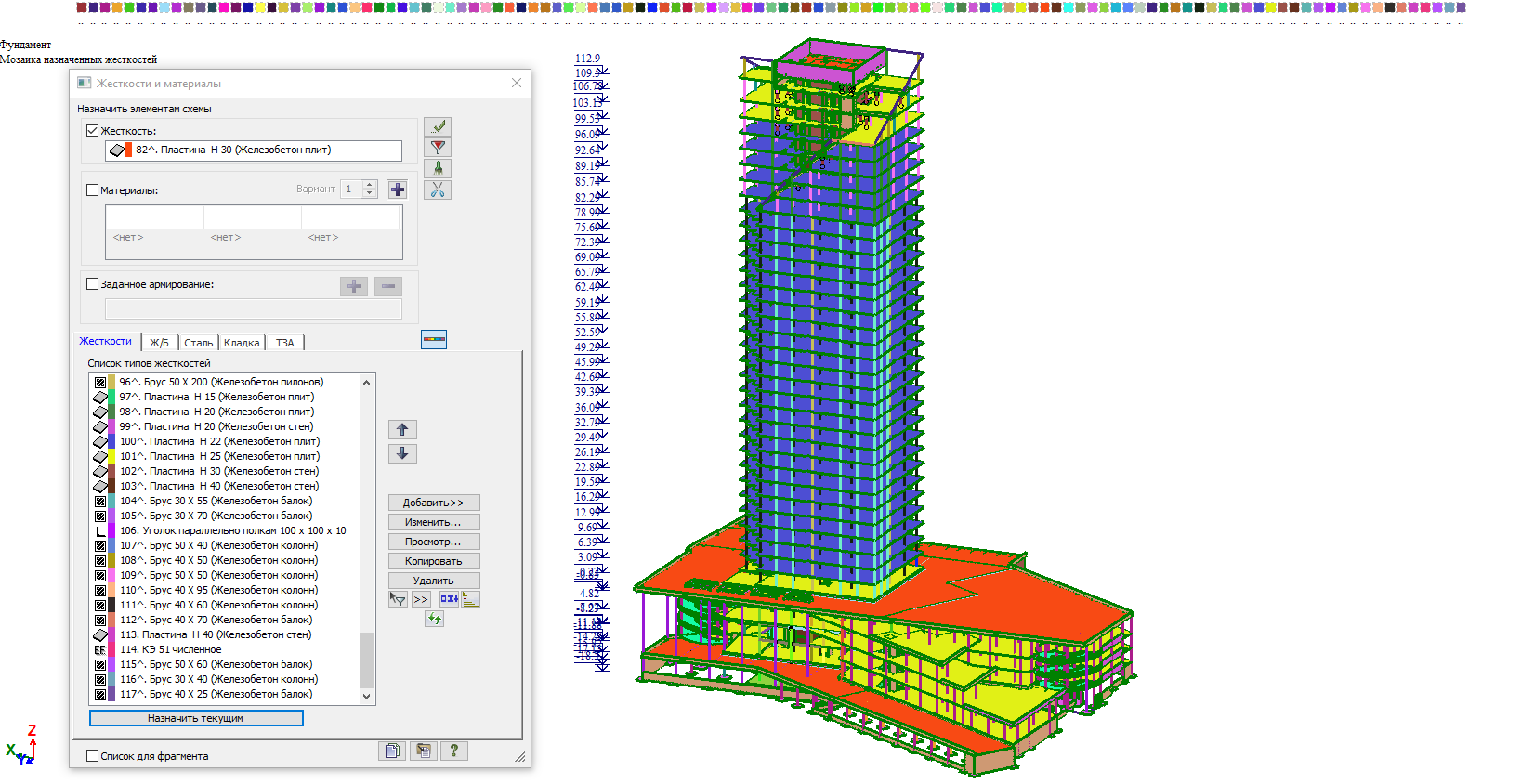
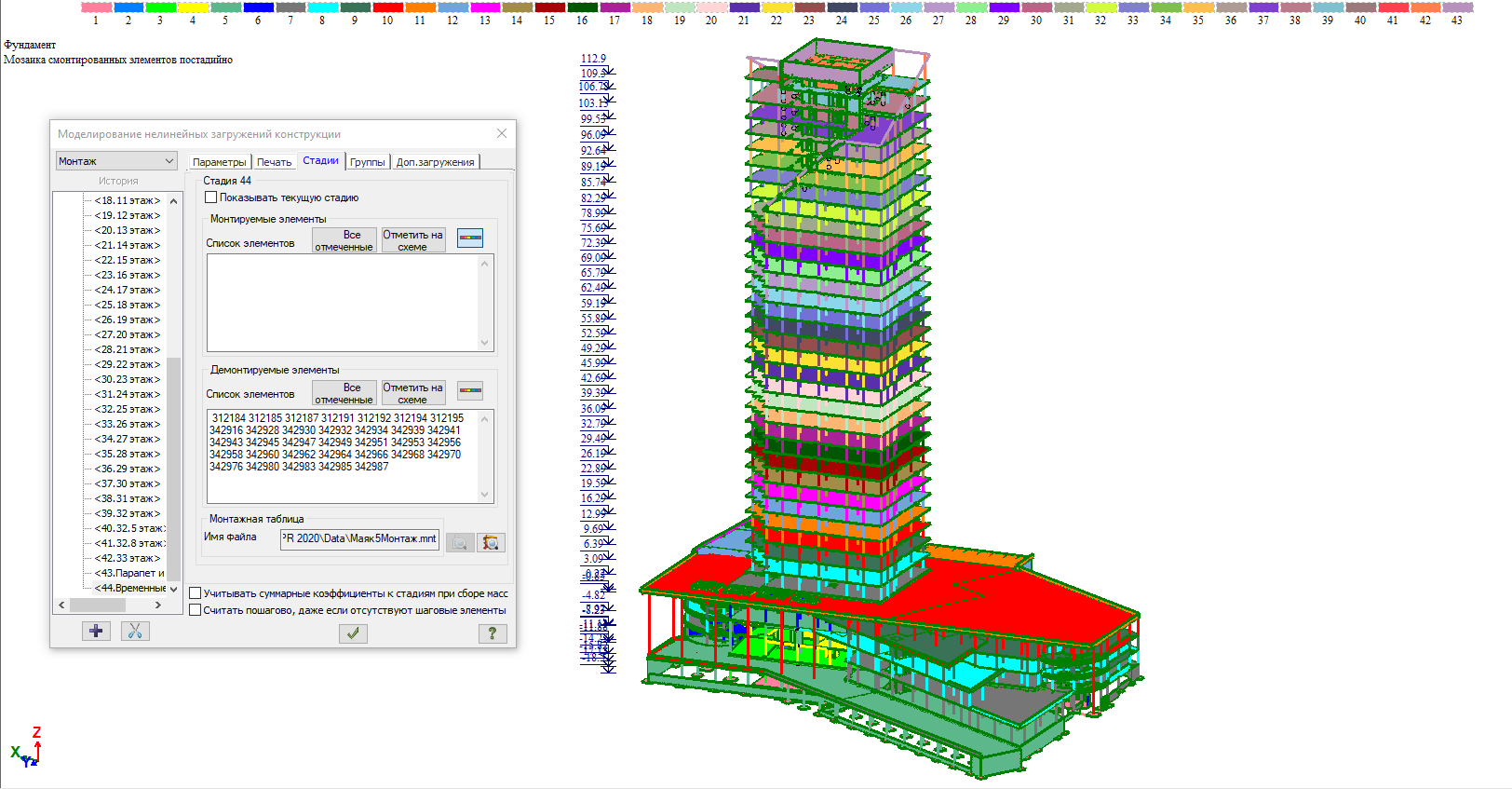
The analysis of the load-bearing elements of the building was carried out in the LIRA-SAPR 2020 multifunctional software for the analysis & design of structures for various purposes by the FEM. Number of nodes in the model: 324180. Number of elements: 342989. The static and nonlinear analyses were carried out. The process of building erection was modelled in the ASSMBLAGE system of the program. The subgrade moduli are obtained from the field tests results of soils
The design model was prepared in the parametric module for 3D modelling (LIRA-CAD module for 3D modelling in LIRA-SAPR 2020 software). The architectural BIM model created in Revit was imported to LIRA-CAD module through the IFC format. Then, because of a large number of changes, the work with the design model was done only in the LIRA-SAPR 2020 software.
Object name
New construction of an apartment building with built-in non-residential premises and parking on Sicheslavska Naberezhna, near the house No. 39 in Dnipro city.
Description
Parameters of the building
- coefficient of responsibility of the residential building — ÑÑ3;
- category of responsibility for the load-bearing structures in a framework — "A";
- safety factor — 1.25;
- life time for the building – 100 years;
- environment inside the building is not aggressive, the building is heated.
Key solutions for design
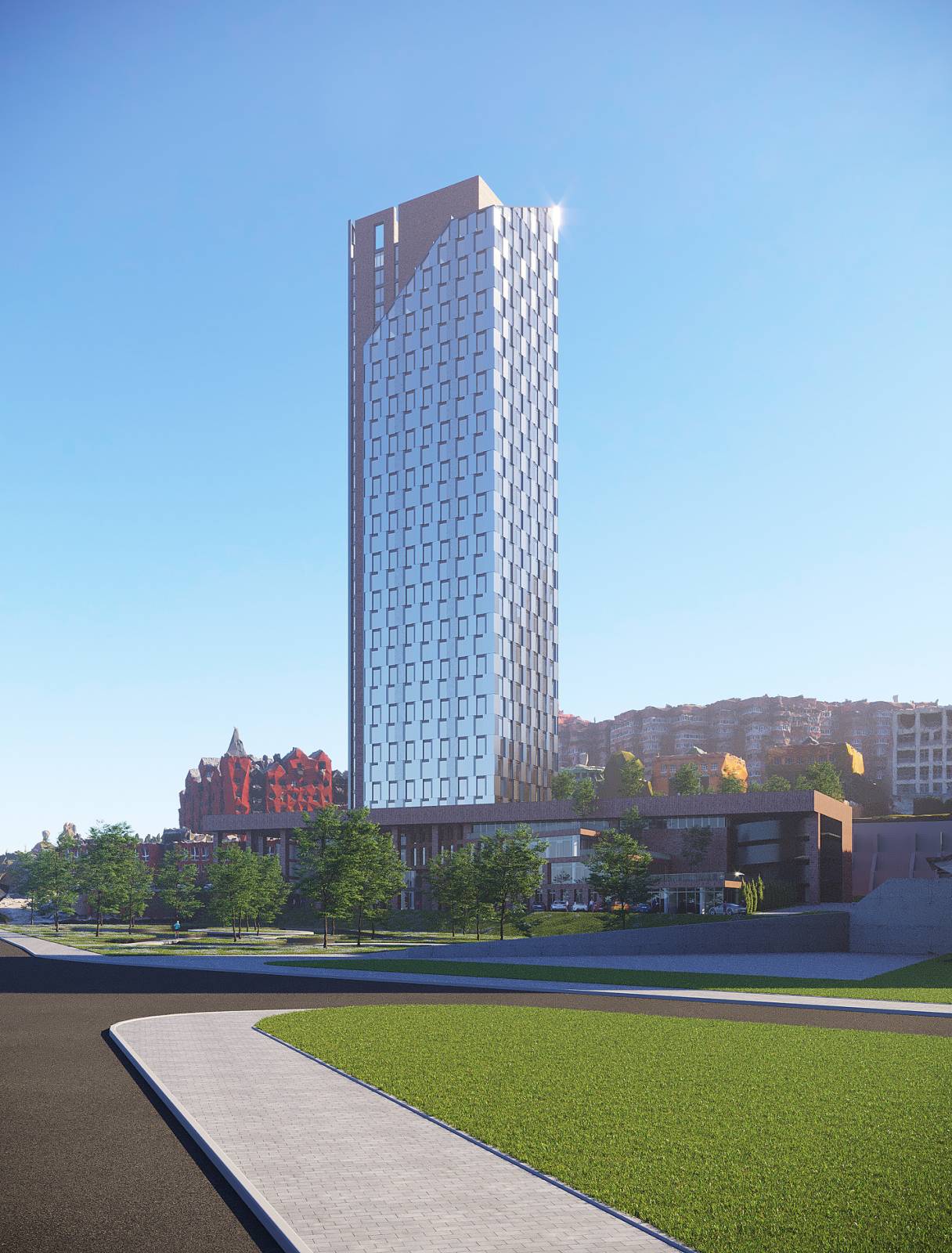
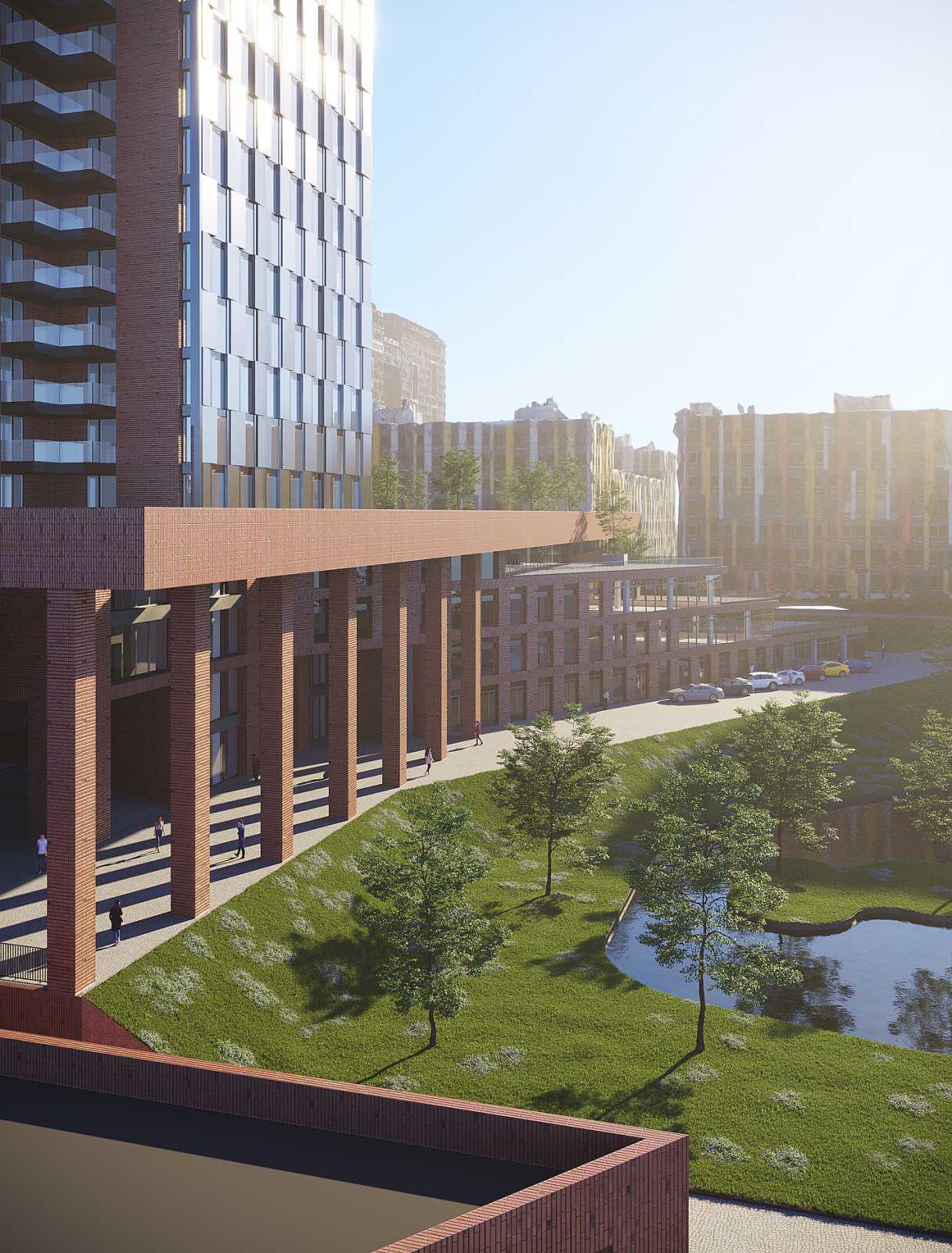
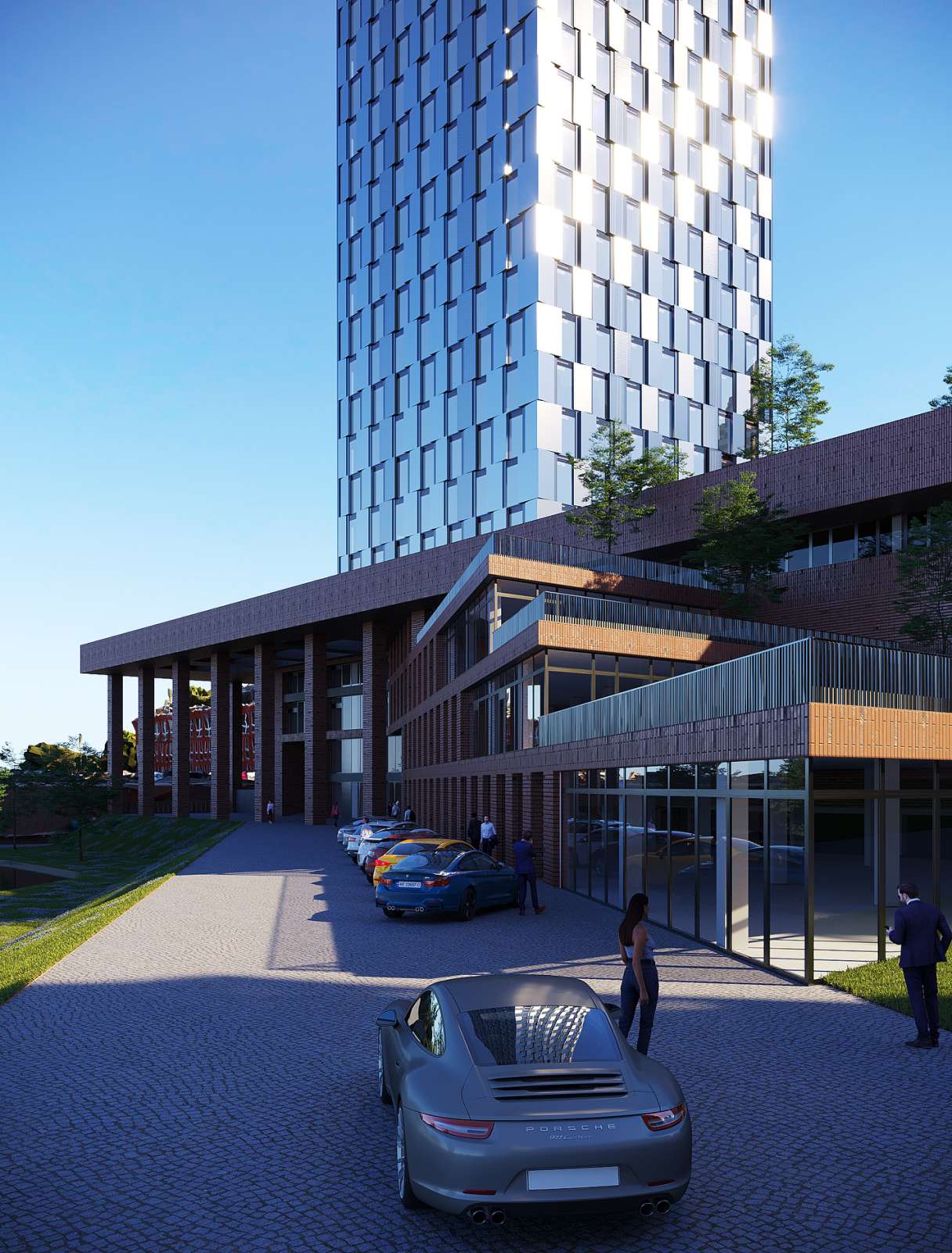
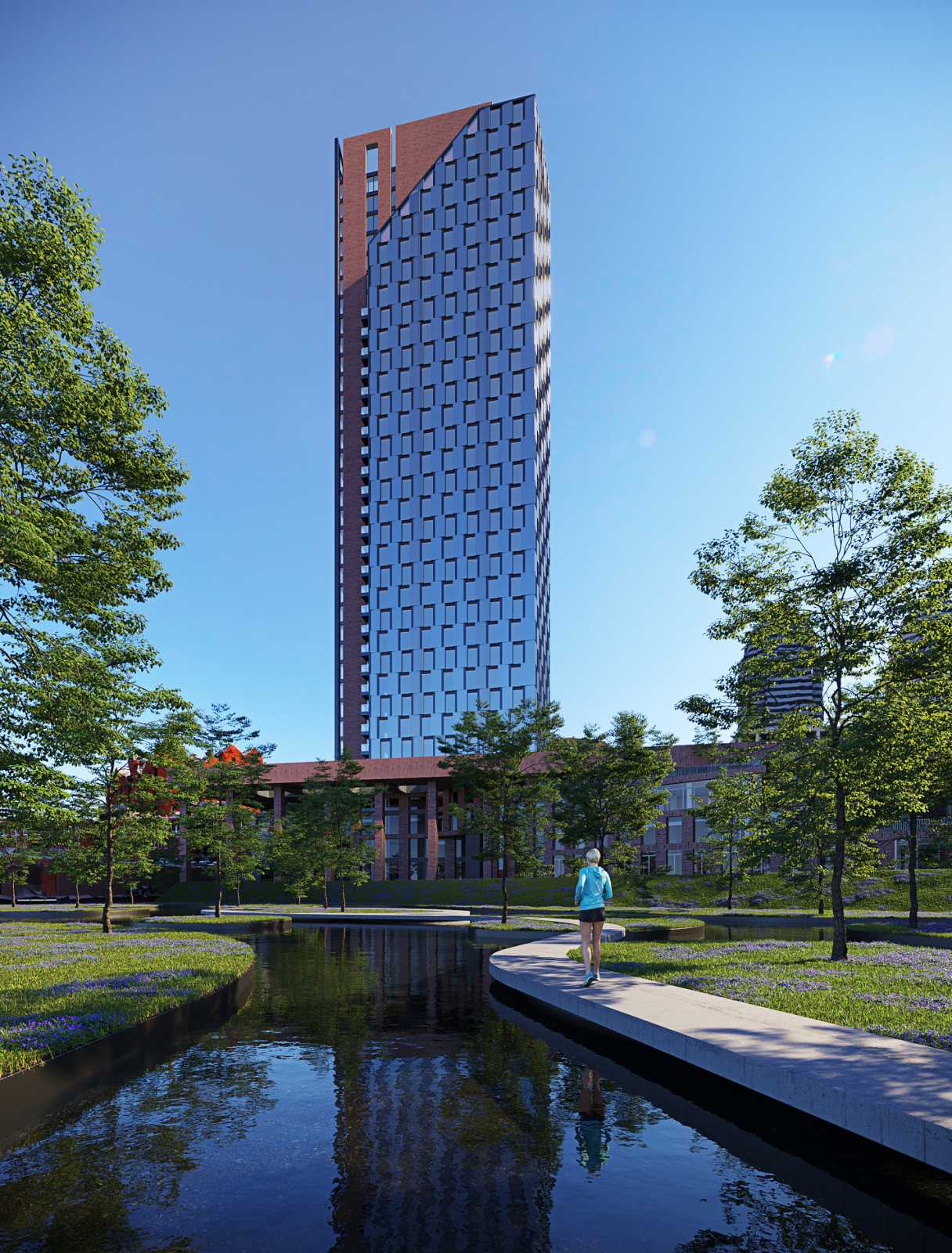
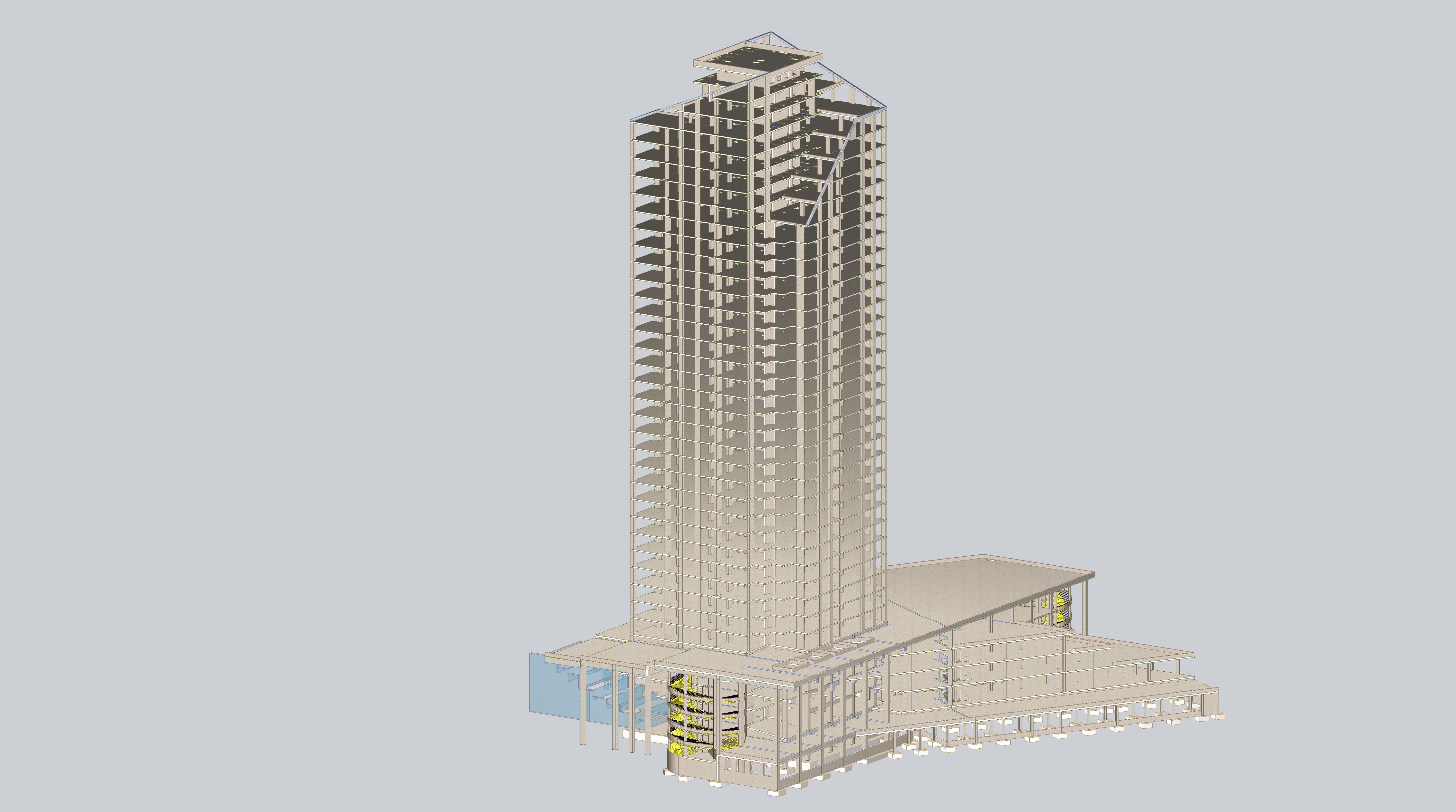
A high-rise portion of a 32-story building (the second complex) and a 5-level substructure (the first complex), which in turn consists of parking and non-residential premises, make up the residential building with built-in non-residential premises.
Non-residential premises are located on the ground floor of the high-rise part of the complex. On the 2nd–30th storeys, there are 1- and 2-room residential apartments; on the 31st–32nd storeys, there are 2 duplex apartments.
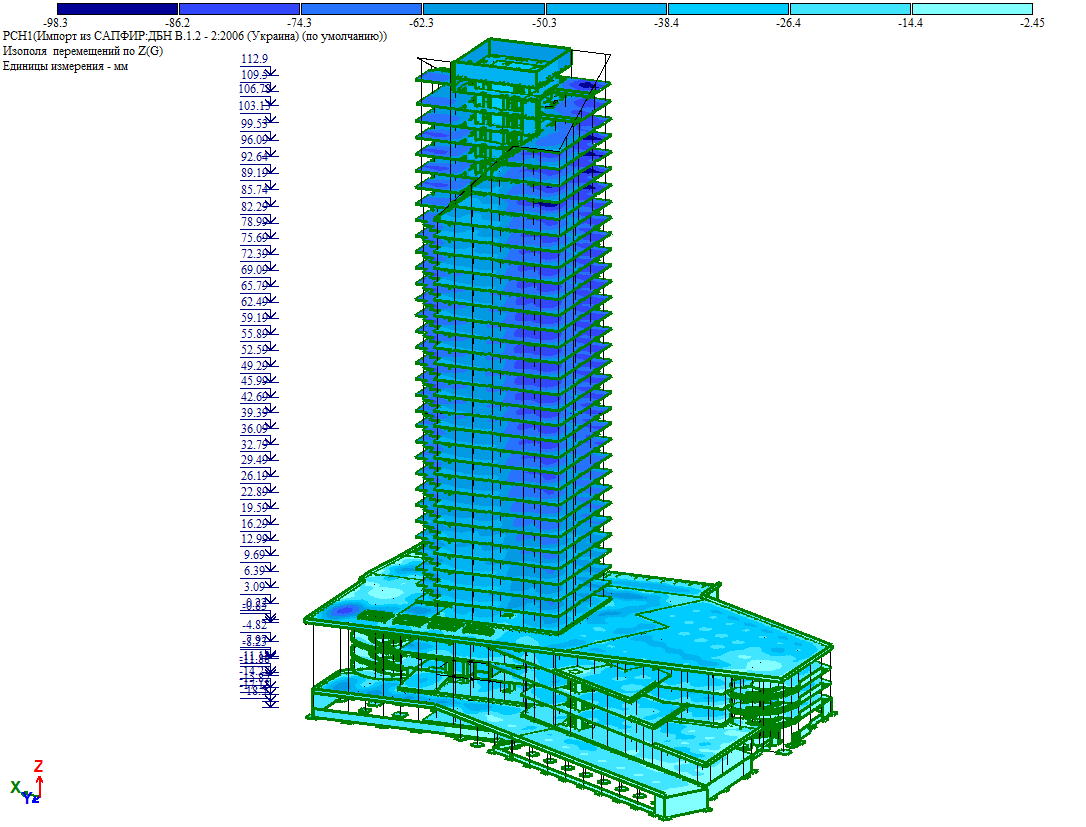
The conventional elevation of the building is 99.80 m. In the Baltic Altitude System, the absolute elevation of 76.50 m is considered to be 0.000. According to the Baltic Altitude System, the building's highest point is 188.35 m.
The total number of apartments in the complex is 314. The total area of the apartments in the complex is 21566.58 m2.
Design solutions
The building consists of a high-rise part and a substructure part. The substructure part is 5 storeys high, while the high-rise part has 32 storeys and a boiler room. The high-rise part is separated from the substructure by expansion joints. The substructure, in turn, is also divided into expansion parts.
The structural model of the building is a monolithic reinforced concrete frame created by vertical load-bearing elements (monolithic reinforced concrete diaphragms and columns) and horizontal elements (monolithic reinforced concrete floor slabs and roofs).
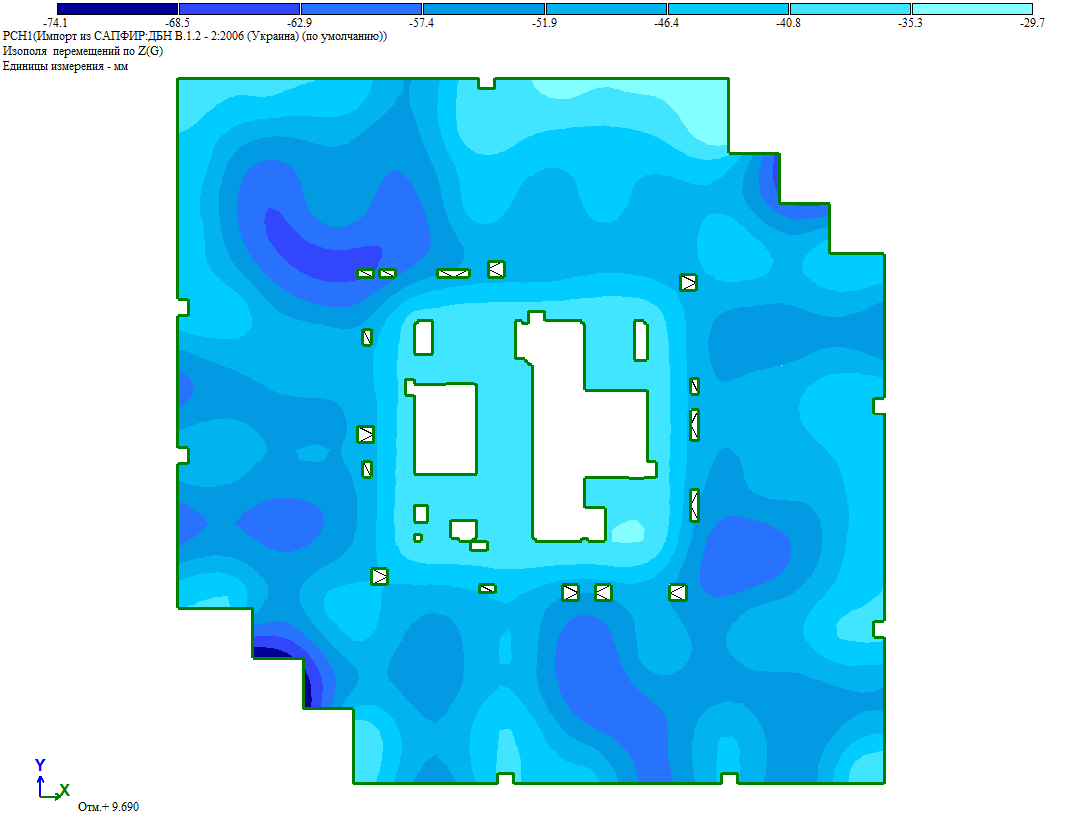
The foundations are slab and isolated footings on a natural base.
The rigid horizontal discs of the floors, the stiffening core, and the walls, from which the loads are transferred to the monolithic reinforced concrete foundations, behave together to ensure the 3D stiffness and geometric stability of the building.
Parameters of structural elements
Foundations
The foundations of the high-rise part are monolithic reinforced concrete slabs with a thickness of 1500 mm. The foundations of the substructure part are monolithic reinforced concrete columns with a height that depends on the depth of the foundation. Grillage materials: C25/30 class of concrete, A500C class of reinforcement according to DSTU 3760:2019. Wired mesh reinforcement is applied.
The basis for isolated footings is the deep zone of the weathering crust of rocks - "movable" and coarse-grained (deep) formations with fine aggregate IGE-6 or the dispersed zone of the weathering crust of rocks IGE-5 if its further development is impossible.
The foundation slab is based on the deep zone of the weathering crust of rocks - "movable" and coarse-grained (deep) formations with fine aggregate IGE-6.
Shear walls
Shear walls are monolithic reinforced concrete with a thickness of 300 and 400 mm. Materials of the walls: concrete of classes C25/30, C30/35, C35/40, reinforcement of class A500C according to DSTU 3760:2019. Wired mesh reinforcement is applied.
Columns
The columns of the high-rise part are monolithic reinforced concrete with a cross-section of 500x900, 700x950, 500x1500, 500x2000 mm. Columns of the substructure part are monolithic reinforced concrete with a section of 400x400, 800x800 mm. Column materials: concrete classes C25/30, C30/35, C35/40, reinforcement class A500C according to DSTU 3760:2019. Wired reinforcing cages are applied.
Stairs
The stairs are monolithic reinforced concrete. The thickness of the flight is 150 mm, the intermediate platforms are 200 mm. Staircase materials: concrete of class C25/30, reinforcement of class A500C according to DSTU 3760:2019. Wired mesh reinforcement is applied.
Floor slabs
The floor slabs - monolithic reinforced concrete slabs with a thickness of 220, 250, 300 mm. Slab materials: concrete of class C25/30, reinforcement of class A500C according to DSTU 3760:2019. Wired mesh reinforcement is applied.
Peculiar features
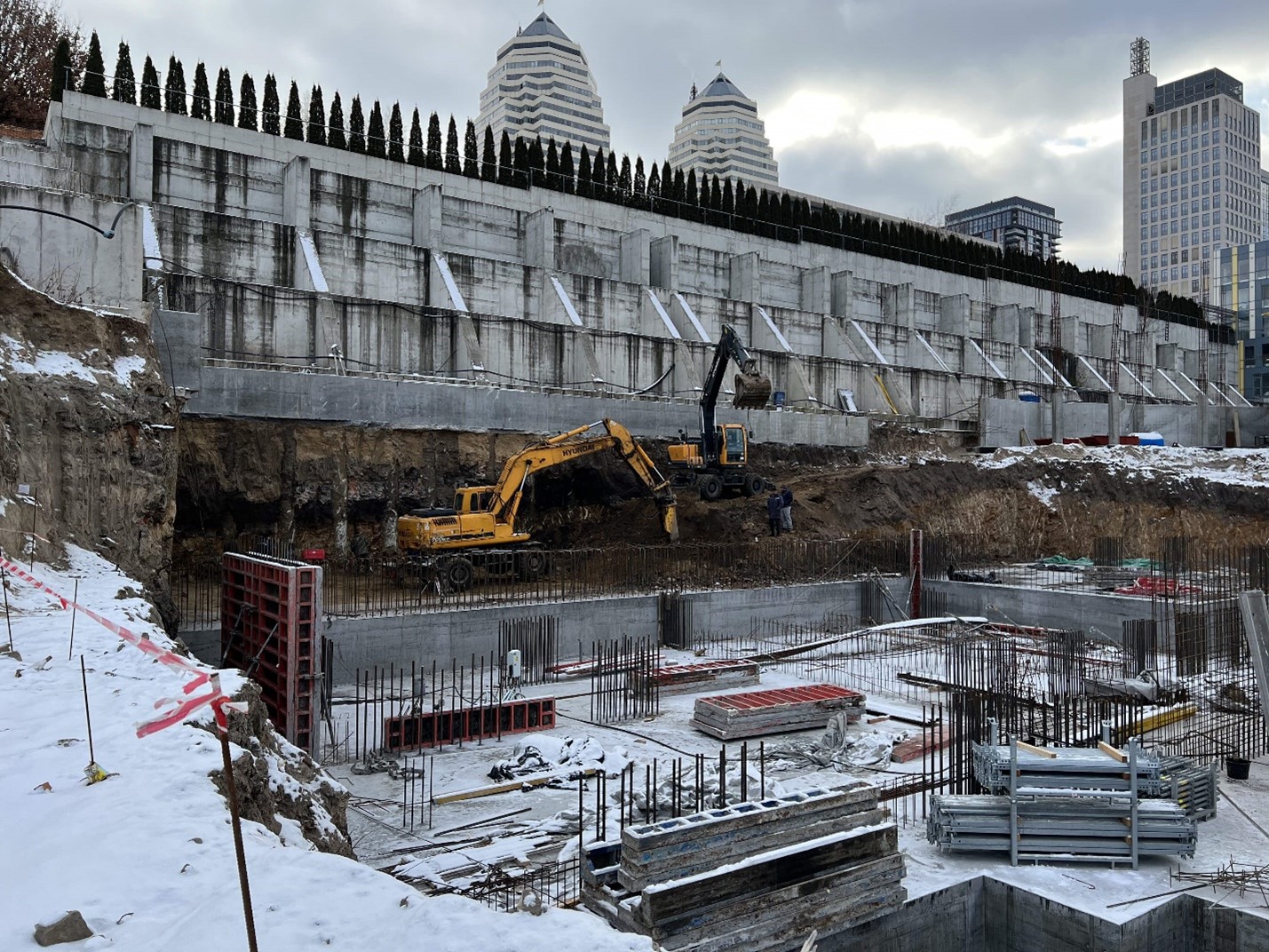
The substructure of the building partially rests on the structures of the existing retaining walls. The high-rise portion of the structure is situated next to an existing retaining wall, which presented a challenge during construction. Before excavation started, bored-injection piles were installed close to the wall to prevent it from sliding during construction, and the grillage was placed beneath the retaining wall components. The following image displays the piles and grillage:
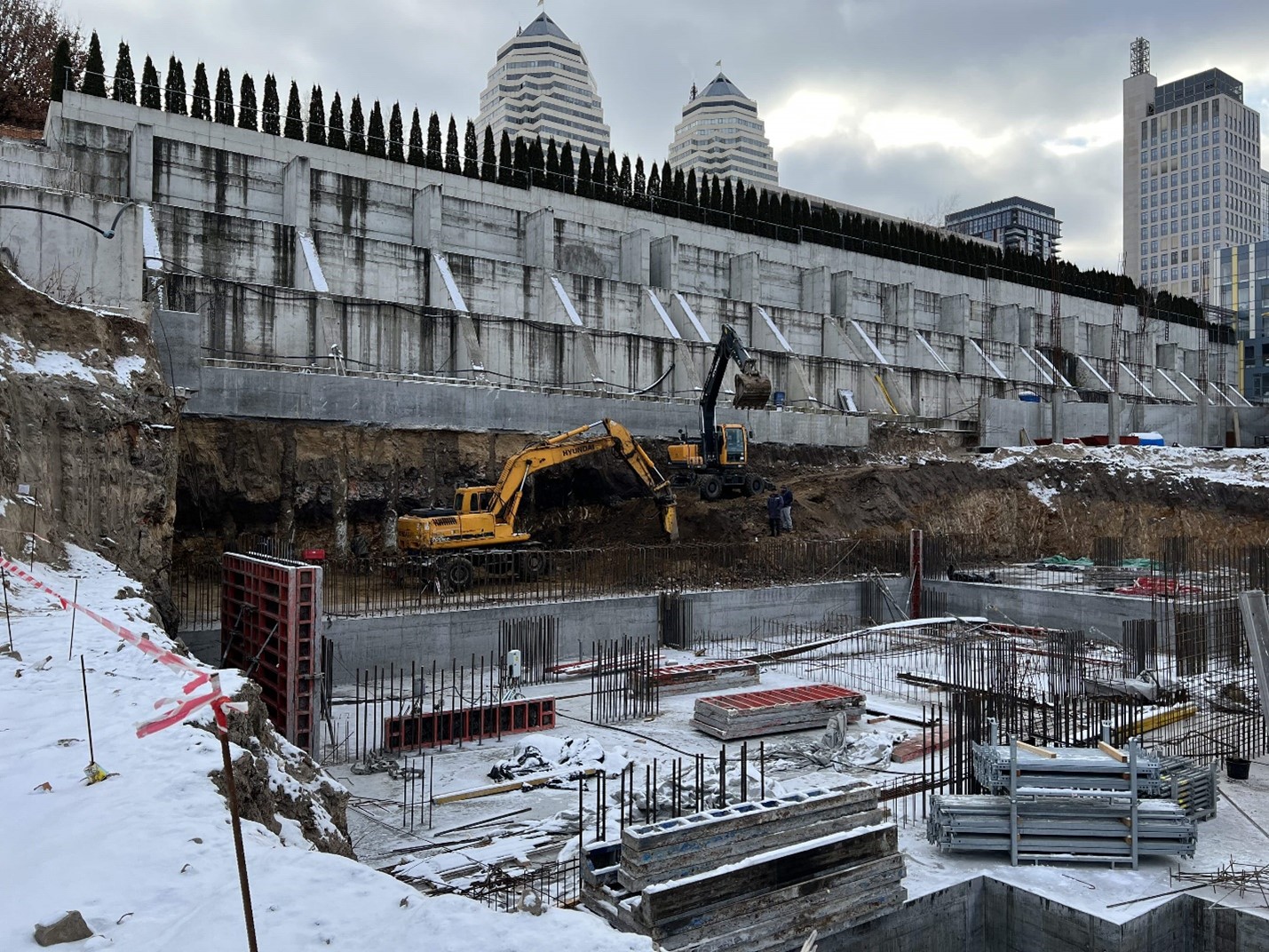

The object has the 15 m high columns of the substructure and cantilever beams with a 4 m high substructure slab. A technology for making working joints was developed for the stage-by-stage erection of the columns.
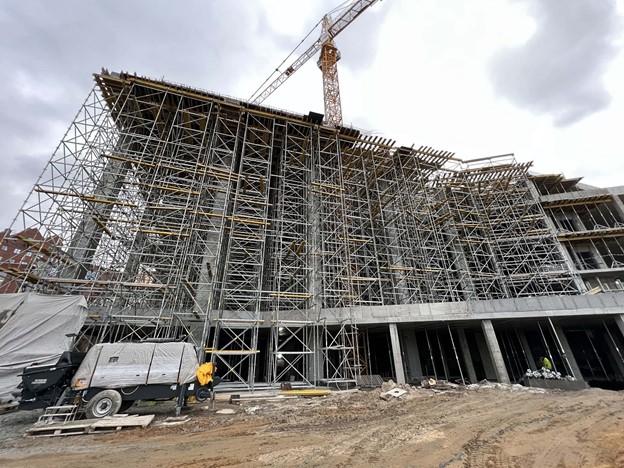

The deep zone of the weathering rock crust forms the foundations; these are "movable" and coarse-grained (deep) formations with highly irregular fine aggregate. The design of foundations for the columns of the substructure was carried out "after the fact", that is, first a foundation pit was excavated, the level of coarse soil was determined, and then the foundation was designed. So, almost all the foundations of the project are different
Full-scale soil testing were conducted with the Prydniprovska State Academy of Civil Engineering and Architecture's cooperation in order to determine the strength and strain properties of the soil. A flat-base stamp of 5000 cm2 was used in the tests. The Prydniprovska State Academy offers scientific assistance to the building construction over the construction phase.
Evaluate the software
If you have any doubt, download the Demo version and evaluate the program or contact our Support Team for more details.



















Comments